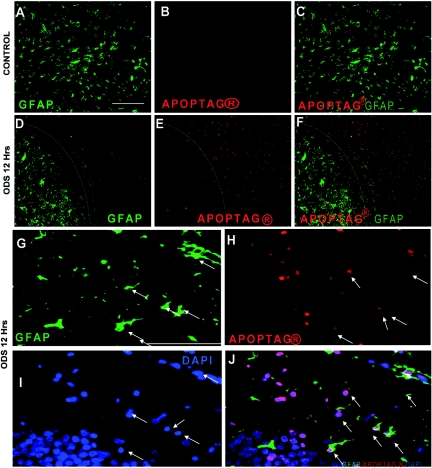
Figure 2.
Astrocyte apoptosis occurs early in osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS). Double immunofluorescence for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (green) and DNA damage (Apoptag® in red) showing homogenous GFAP staining in uncorrected control rats with no apoptotic cells (A through C). In contrast, 12 hours after correction of hyponatremia (D), a crisp demarcation (white line) distinguishes the astrocyte-depleted region from the adjacent regions containing undisturbed astrocytes. As shown in (E) and (F), the astrocyte-depleted region is strongly positive for DNA damage and also displays a clear delineation from the normal, nonapoptotic region (white line). At higher magnification, degenerating astrocytes stain positive for GFAP (G) but have lost their characteristic shape. Many apoptotic nuclei (H) also show bright staining for 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (I), and in (J) these cells colocalize with GFAP-positive cells (arrows). The scale bar is 100 μm.