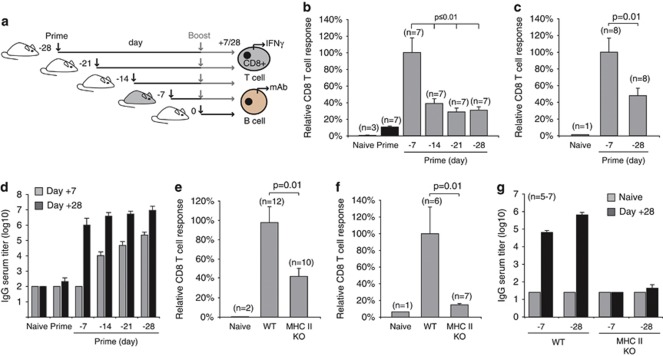
Figure 2.
Cellular and humoral immune responses to ISCOMATRIX vaccines are dependent on CD4+ T-cell help. (a) Schematic showing the dosing regimen used to evaluate vaccine antigen-specific CD8+ T cell and antibody response. (b) IFN-γ production by endogenous OVA-specific CD8+ T cells was determined in the spleen 7 days after the boost vaccination. (c) IFN-γ production by endogenous gB (HSV-1)-specific CD8+ T cells was determined in the spleen 7 days after the boost vaccination. Results in (b, c) are expressed relative to the response obtained with a day −7, 0-dosing regimen. Mean values are expressed ±s.e.m.. Student's t-test was used to calculate statistical significance. (d) OVA-specific antibody titers (total IgG) in serum collected from mice vaccinated with the dosing protocols shown in (a). OVA-specific titers were quantified 7 or 28 days after the final vaccine dose. (e) OVA-specific CD8+ T-cell responses were compared in wild type (WT) and MHC class II-deficient mice (MHC II KO) vaccinated on days −7, 0. (f) The OVA-specific ‘recall' CD8+ T-cell response was assessed using a 5-day ex vivo re-stimulation protocol. (g) OVA-specific IgG titers in serum collected from naïve WT or MHC II KO vaccinated with two different vaccine dosing regimens. All results are representative of at least two or more independent experiments. ‘Student's' t-test was used to calculate statistical significance.