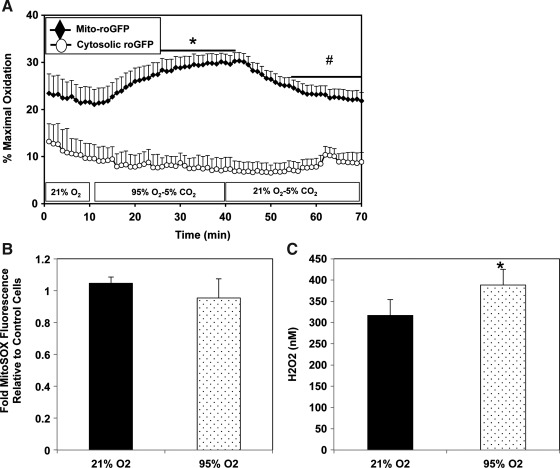
FIG. 4.
Exposure to hyperoxia induces mitochondrial matrix H2O2 in FPASMC. (A) The redox sensor roGFP was used to assess oxidant levels in cytosol and mitochondrial matrix. Surface-exposed cysteine residues are sensitive to the local redox environment. After obtaining ratiometric measurements of roGFP, the sensor was calibrated by maximally reducing it with dithiothreitol (DTT, 1 mM) and maximally oxidizing it with t-butyl hydroperoxide (TBH, 1 mM) to yield percent oxidation. FPASMC were plated on collagen-coated cover slips and were exposed in a flow-through chamber on an epifluorescence microscope to 95% O2/5% CO2 for 30 min, followed by a 30-min recovery period in 21% O2/5% CO2. Data shown are from 19 cells from four coverslips for mito-roGFP and 7 cells from five coverslips for cytosolic roGFP. *p<0.05 vs. FPASMC baseline oxidation in 21% O2/5% CO2; #p<0.05 vs. FPASMC maximal oxidation in 95% O2/5% CO2. (B) FPASMC were loaded with MitoSOX, a fluorescent mitochondrially targeted superoxide sensor, prior to 30 min of exposure to 95% O2/5% CO2 (n=10, measured in duplicate). (C) FPASMC were exposed to 95% O2/5% CO2 for 30 min, and intracellular H2O2 was quantified with Amplex Red fluorescence (n=8, *p<0.05 vs. FPASMC in 21% O2/5% CO2).