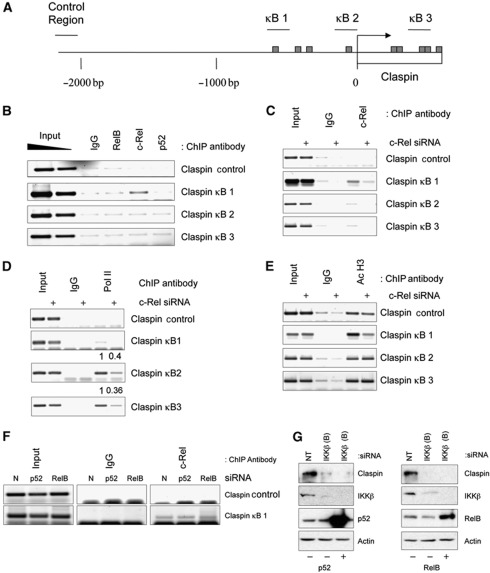
Figure 3.
The Claspin gene promoter is directly regulated by c-Rel. (A) Schematic of the human Claspin gene promoter with putative NF-κB sites represented as bars, and ChIP PCR primer sets represented as lines. (B) ChIP assays using Control IgG, RelB, c-Rel or p52 antibodies were performed on cell extracts from U2OS cells. Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR amplified using the indicated primer pairs alongside 2% input genomic DNA. (C) ChIP assays using Control IgG and c-Rel antibodies were performed on cell extract from control or cells depleted of c-Rel. Immunoprecipitated DNA was amplified by PCR using the indicated primer pairs. (D) As in (C) but ChIP was performed using antibodies directed against RNA polymerase II. (E) As in (C) but ChIP was performed using antibodies directed against acetylated histone H3. Levels of RNA polymerase II recruitment to the κB sites of the Claspin gene were quantified, normalized to inputs, and numbers indicate the difference between control and c-Rel-depleted samples. (F) ChIP assays using Control IgG and c-Rel antibodies were performed on cell extract from control or cells depleted of p52 or RelB. Immunoprecipitated DNA was amplified by PCR using the indicated primer pairs. (G) U2OS cells were co-transfected with a non-targeting siRNA or a siRNA to deplete IKKβ, along with either a vector control or a p52 or RelB expression constructs, as indicated. WCLs were prepared and analysed by western blot using the indicated antibodies.