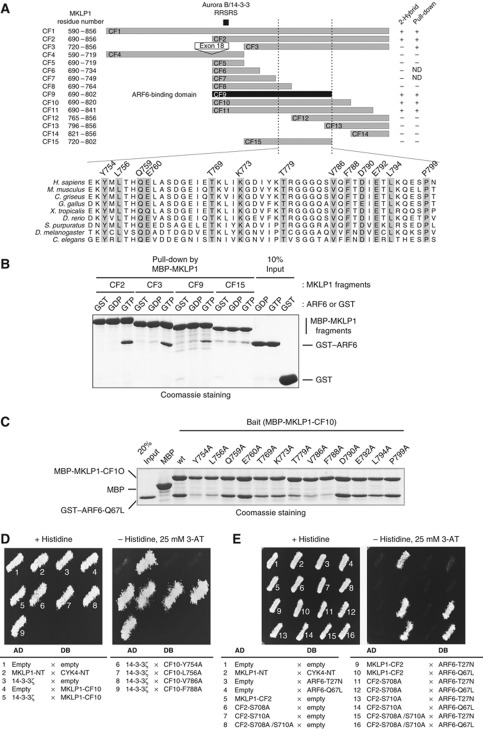
Figure 3.
ARF6 and 14-3-3 interact with MKLP1 through overlapping, but not identical, regions in the MKLP1 C-terminal tail. (A) Schematic representation of MKLP1 fragments examined for the interaction with ARF6 by Y2H and in-vitro pull-down assays. (B) In-vitro pull-down assay to test ARF6-binding by MKLP1 fragments. GST–ARF6 Q67L (GTP), T27N (GDP) or GST alone (GST) was pulled down by the MKLP1 fragments (CF2, CF3, CF9 or CF15) tagged with maltose-binding protein (MBP) immobilised on amylose beads (New England Biolabs). (C) Alanine substitutions at the conserved residues in the C-terminal half of the minimum ARF6-binding domain and their effects on the MKLP1–ARF6 interaction. ARF6 Q67L was pulled down by the amylose beads immobilised with the MBP-MKLP1-CF10 fragments containing the indicated mutations. (D, E) Y2H assays to test the effects of the MKLP1 mutations in the ARF6-binding domain on the interaction with 14-3-3 (D) and of the mutations in the Aurora B/14-3-3 motif on the interaction with ARF6 (E). Growth on medium lacking histidine and supplemented with 3-aminotriazol (3AT) indicates an interaction between proteins fused to the activation domain (AD) and DNA-binding domain (DB). The mutations at Y754, L756, V786 and F788 specifically disrupt the MKLP1–ARF6 interaction without affecting the MKLP1–14-3-3 interaction while S708 and S710 mutations do not interfere with the MKLP1–ARF6 interaction.