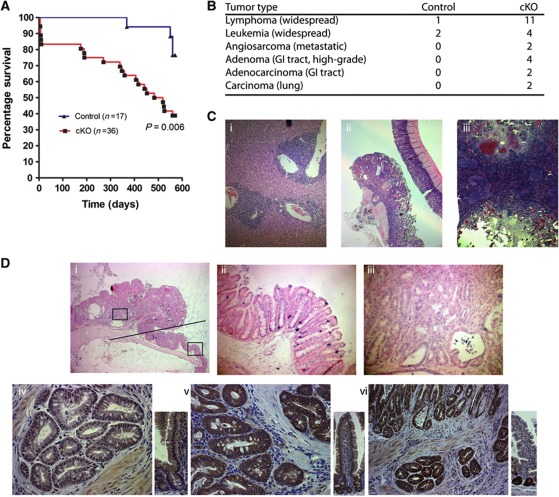
Figure 5.
Nrbp1 is a tumour suppressor in vivo. (A) Survival analysis of cKO (NrbpfloxRosaCreERT2/+) and control mice (Nrbpflox/+RosaCreERT2/+ and Nrbpflox/floxRosa+/+) after treatment with 1 mg tamoxifen per day for 4 days. Animals became moribund and were culled as a result of either an ‘early Nrbp1 loss phenotype’ (animals <10 days post treatment) or when they developed macro/microscopically visible tumour(s) (animals >10 days post treatment). (B) Table provides a summary of the tumour types found in the mice (some animals had more than one type of tumour). (C) H&E staining of tissues from cKO mice showing (i) widespread lymphoma in the liver ( × 100 magnification), (ii) invasive colorectal adenocarcinoma ( × 250 magnification) and (iii) high-grade angiosarcoma in the spleen ( × 250 magnification). (D) ISH analysis of Nrbp1 in a colorectal lesion from an Nrbp1floxRosaCreERT2/+ mouse shows (i) a tumour area left of the black line, and normal colonic tissue right of the black line ( × 25 magnification), with the lower box enlarged in (ii) and the upper box enlarged in (iii), showing reduced Nrbp1 expression levels in tumour tissue ( × 200 magnification). Immunohistochemical analysis of an invasive colorectal adenocarcinoma from an Nrbp1floxRosaCreERT2/+ mouse showing significant strongly positive staining with (iv) c-Myc ( × 400 magnification) and (vi) pErk ( × 200 magnification) antibodies, but (v) no increased nuclear Ctnnb1 signal ( × 400 magnification).