FIGURE 1.
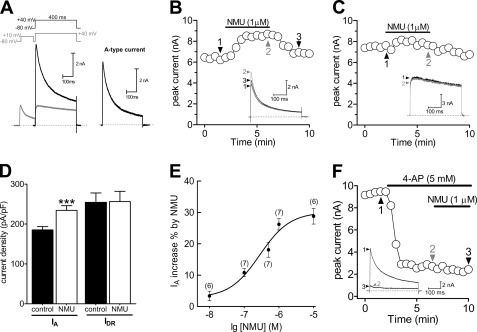
NMU selectively increased IA in small DRG neurons. A, isolation of IA. Na+ currents, Ca2+ currents, and Ca2+-activated K+ currents have been eliminated (see “Experimental Procedures”). Left, the membrane voltage was held at −80 mV and IA was isolated by a two-step voltage protocol. Right, the remaining current after off-line subtraction of the noninactivating portion of current remaining after the prepulse to −10 mV. This protocol is used for isolation of IA in all figures. B and C, representative current traces and the time course showed that IA (n = 7, B), but not sustained delayed rectifier K+ current (IDR) (n = 9, C), was significantly increased during exposure to 1 μm NMU. D, summary data of current density showed that 1 μm NMU selectively increased IA. E, dose-response curve for the stimulatory effects of NMU on IA. The line represents the best fit of the data points to the sigmoidal Hill equation. Number of cells tested at each concentration of NMU is indicated in parentheses. F, time course and exemplary traces showed no effect of 1 μm NMU on IA in the presence of 4-AP (n = 5). ***, p < 0.001 versus control.