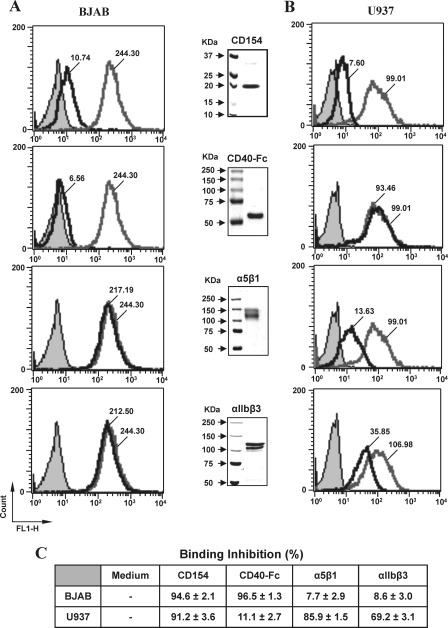
FIGURE 2.
CD154 binding to U937 cells is inhibited by soluble α5β1 and αIIbβ3, whereas binding to BJAB cells is inhibited by sCD40. BJAB (A) or U937 cells (B) were incubated for 1 h with labeled rsCD154-Alexa (200 ng/ml) in the absence (Media) or presence of 2 μg/ml of sCD154, sCD40-Fc, α5β1, or αIIbβ3. For competition analysis with CD154, cells were preincubated with 10-fold molar excess of uncoupled sCD154 (2 μg/ml) prior to incubation with labeled rsCD154-Alexa (200 ng/ml), although CD40-Fc, α5β1, and αIIbβ3 were co-incubated with labeled rsCD154-Alexa prior to incubation with cells. Cells were then washed and analyzed by flow cytometry for CD154 binding. Filled gray plots indicate avidin-Alexa staining (negative control); empty gray plots show the binding of rsCD154-Alexa in the absence of competitors; and empty black plots represent rsCD154-Alexa binding in the presence of unlabeled competitors (CD154, CD40-Fc, α5β1, or αIIbβ3). Values within plots represent the mean fluorescence intensity for rsCD154-Alexa binding in the absence or presence of unlabeled competitors. Middle blots show the expression of the recombinant competitors. Proteins (2 μg total) were resolved on 6% (CD40-Fc, α5β1, and αIIbβ3) or 12% (CD154) SDS-polyacrylamide gels and stained with Coomassie Blue (R-250). Data presented in C show the mean percentage of inhibition (±S.E.) in the presence of unlabeled competitors. All results shown are representative of four independent experiments.