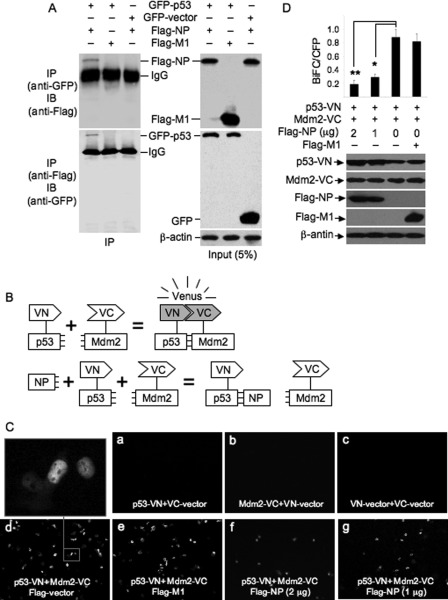
FIGURE 7.
Detection of viral NP-p53 interaction and BiFC analysis of the effect of viral NP on interaction between p53 and Mdm2. A, H1299 cells were transiently transfected with a combination of the indicated plasmids and incubated for 16 h. The cell lysates prepared from the transfectants were subjected to co-immunoprecipitation assay using anti-GFP and anti-Flag antibodies. The immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (left panels). The cell lysates were included as a loading control (right panels). IP, immunoprecipitation. IB, Western blot. B, schematic illustration of BiFC assay of interaction between p53 and Mdm2. VN and VC are the N- and C-terminal fragments of Venus fluorescent protein, respectively. NP, viral nucleoprotein. C, H1299 cells were transiently transfected with a combination of the indicated plasmids and incubated for 13 h. The fluorescence emission was detected using a fluorescence microscope. D, H1299 cells were transiently transfected with a combination of the indicated plasmids and incubated for 13 h. pECFP vector expressing cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) was co-transfected as transfection control. The protein expression in the transfectants was detected by Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. The BiFC efficiencies (BiFC/CFP) in the transfectants were quantified by normalizing the number of Venus-fluorescence-positive cells to the number of CFP-positive cells. The number of cells in ten randomly selected visual fields was counted. Results are presented as the means ± S.E. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 compared with cells transfected with p53-VN and Mdm2-VC.