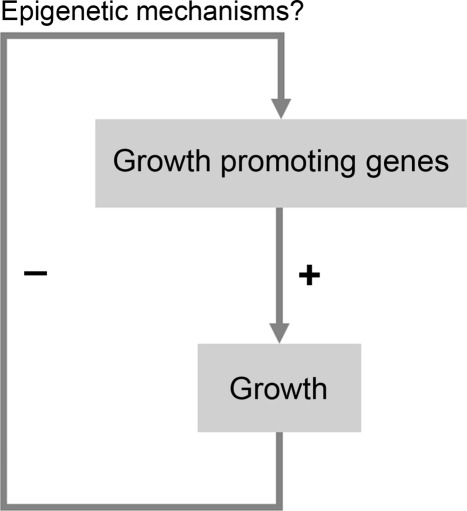
Fig. 4.
Model for a mechanism that restricts juvenile body growth. In early life, multiple growth-promoting genes are well expressed, leading to rapid growth. However, growth causes down-regulation of these growth-promoting genes (perhaps through epigenetic mechanisms) which causes growth to slow. Progression of this negative feedback loop would eventually cause the growth rate to approach zero.