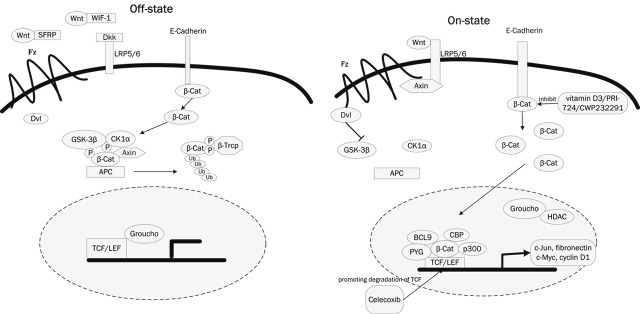
Figure 1.
The Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway and their inhibitors. A: In the off-state, Wnt ligands usually bind with Soluble frizzled-related proteins (SFRP) and Wnt inhibitory factor-1 (WIF-1) which prevent them from interact with frizzled (Fz) receptors. Dickkopf (Dkk) interacts with low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6 (LRP5/6) to inhibit binding of Wnt ligands. β-Catenin that is not bound with cadherin is phosphorylated by a complex formed by casein kinase 1α (CK1α), glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β), adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and Axin, then it is identified by β-TrCP and lead to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. B: In the on state, Wnts bind to and activate FZD (Frizzled) and LRP (LDL-related receptor protein) receptors on target cells. Phosphorylation of β-Catenin is suppressed and β-Catenin escapes from the degradation. Free cytoplasmic β-Catenin translocates to the nucleus, forms a complex with TCF/LEF, and activates the transcription of target genes, such as cyclin D1, c-myc, c-Jun, and fibronectin. The coupounds vitamiD3, PRI-724, CWP232291 inhibit the β-Catenin that lead to the inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway, and Celecoxi worked through promoting degradation of TCF.