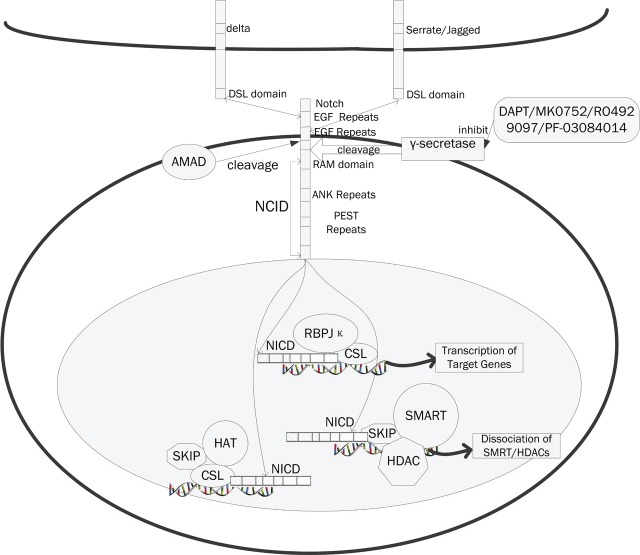
Figure 2.
The Notch signaling pathway and their inhibitors. Notch proteins (and ligands) contain extracellular EGF-like repeats, which interact with the DSL domain of ligands. Activation of Notch upon ligand binding is accompanied by proteolytic processing that releases an intracellular domain of Notch (NICD) from the membrane. The NICD contains the RAM23 domain (RAM), which enhances interaction with CSL protein, NLS (Nuclear Localization Signals), a CDC10/Ankyrin repeat domain ANK. Upon release, the NICD translocates to the nucleus and associates with the CSL family of DNA-binding proteins to form a transcriptional activator, that activate the expression of a set of target genes, including the E (spl) (Enhancer of Split) group and others. The compounds, DAPT, MK0752, RO4929097, PF-03084014, inhibit the Notch signaling pathways through the inhibition of γ-secretase.