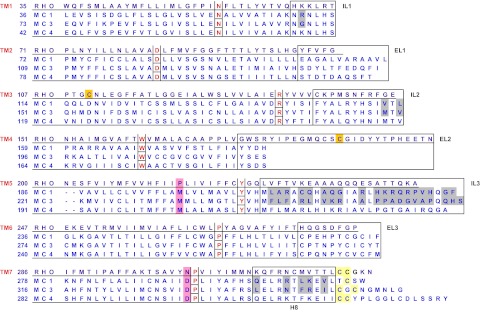
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of bovine rhodopsin (RHO) with human MC1R, MC3R, and MC4R. The ELs and intracellular loops are boxed (note that the C terminus of rhodopsin is not complete). The divergent N termini are not shown here. The most conserved residues in each TM (50 residue) are in red and are boxed individually. The highly conserved Cys residues at the top of TM3 and EL2 in rhodopsin that form a disulfide bridge are highlighted in gold. The potential palmitoylation sites at the C termini are shaded in light yellow. In MCRs, TM5 is two residues shorter than rhodopsin; otherwise, EL2 would consist of only two residues, which is not likely. Note the following unique characteristics of the MCRs, including the absence of the highly conserved disulfide bridge between the EL2 and the top of TM3 (shaded in gold for rhodopsin). The intracellular loops and ELs of the MCRs are short, especially EL2, making MCRs some of the shortest members in the GPCR superfamily. Highly conserved Pro in TM5 and Asn in TM7 (in the NPxxY motif) in family A GPCRs are substituted by a Met and an Asp, respectively, in all MCRs (shaded in rose). In other family A GPCRs, this Asn is proposed to interact with the highly conserved Asp in TM2. In MCRs, Asp is present at both loci, unlikely to interact with each other. GenBank accession numbers for the genes are: bovine rhodopsin, NM_001014890; human MC1R, NM_002386; human MC3R, NM_019888; and human MC4R, NM_005912. IL, Intracellular loop.