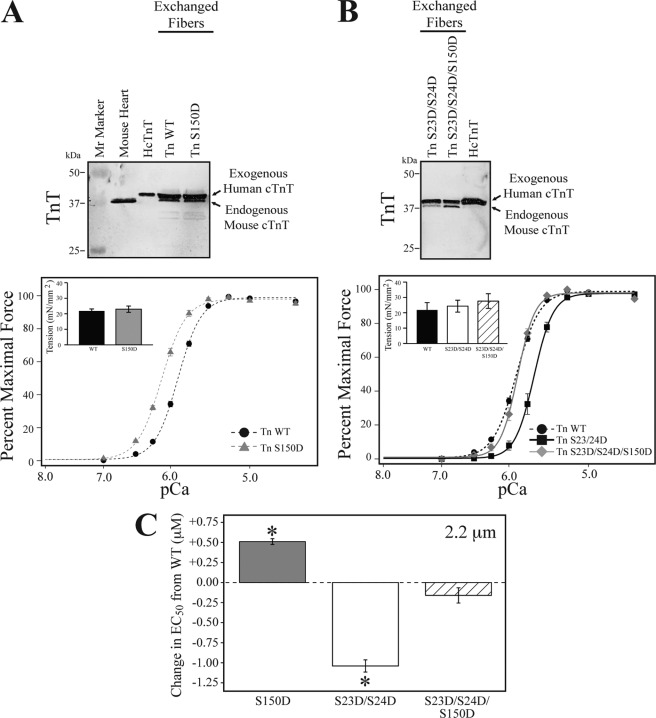
FIGURE 4.
Cardiac TnI Ser-150 phosphorylation increases myofilament Ca2+-sensitive force development and blunts cTnI PKA dependent desensitization. Skinned mouse cardiac fiber bundles were exchanged with human cTn containing either wild-type (Tn WT), Ser-150 (Tn S150D), Ser-23/24 (Tn S23D/S24D), or combined Ser-150 and PKA (Tn S23D/S24D/S150D) pseudo-phosphorylated cTnI. Fiber bundles from individual force experiments were analyzed for cTn exchange by Western blot with a TnT antibody. Representative fibers demonstrate an average of 67% incorporation of the larger molecular mass, exogenous human TnT band that was not different in any of the exchanged groups. A, average tension-Ca2+ measurements of fiber bundles at 2.2 μm exchanged with Tn S150D (gray triangle, dashed line) exhibit increased Ca2+ sensitivity compared with Tn WT (black circles, dashed line) exchange in the absence of an effect on Hill coefficient or maximal force development (inset). B, fiber bundles exchanged with Tn S23D/S24D (black square, solid line) demonstrate the expected decrease in Ca2+ sensitivity compared with Tn WT. Exchange of the cTnI Tn S23D/S24D/S150D (gray diamond, solid line) did not exhibit altered Ca2+ sensitivity compared with Tn WT; however, Tn S23D/S24D/S150D Ca2+ sensitivity was increased compared with that of Tn S23D/S24D exchange. Tn S23D/S24D/S150D exchange did not alter the Hill coefficient or maximal force development (inset). C, the change in EC50 at 2.2 μm of the various exchanged cTn from that of WT demonstrates Tn S150D (gray bar) increased EC50 by 0.51 μm from Tn WT, whereas combination of S150D with S23D/S24D phosphorylation (hatched bar) was not different from Tn WT and blunted the −1.05 μm decrease in EC50 of cTnI S23D/S24D (white bar) exchange alone. Gray, Tn S150D; white, Tn S23D/S24D; hatched, Tn S23D/S24D/S150D. *, ANOVA Bonferroni EC50 p < 0.05 versus WT.