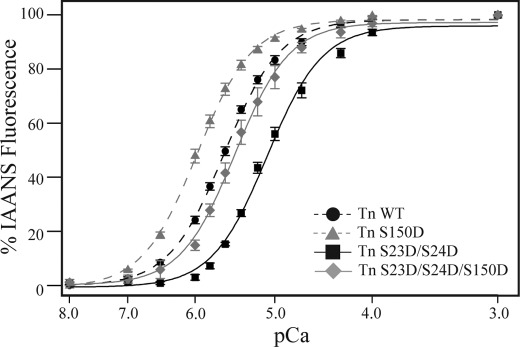
FIGURE 5.
The cTnI Ser-150 phosphorylation-induced increase in submaximal force development results from increased Ca2+ binding to TnC. Steady-state Ca2+ binding to TnC was determined by IAANS-labeled TnC fluorescence of thin filaments reconstituted with cTn containing either wild-type (Tn WT; black circle, black dashed line), Ser-150 (Tn S150D; gray triangle, gray dashed line), PKA (Tn S23D/S24D; black square, black solid line), or combined Ser-150 with PKA (Tn S23D/S24D/S150D; gray diamond, gray solid line) pseudophosphorylated cTnI. Similar to Ca2+-regulated force development, Tn S150D-reconstituted thin filaments exhibit increased Ca2+ binding to TnC compared with WT. Calcium binding in thin filaments containing Tn S23D/S24D was decreased, whereas the combined Tn S23D/S24D/S150D filaments were not different from WT.