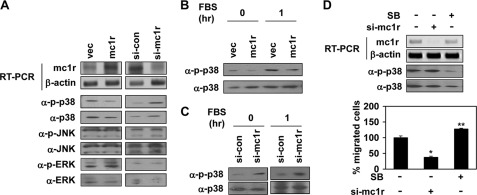
FIGURE 5.
MC1R inhibits activation of p38. A, B16F10 cells were transfected with either vector (vec) or MC1R (mc1r, left panels) and either control siRNA (si-con) or siRNA targeting MC1R (si-mc1r, right panels). Expression mRNA level of MC1R was analyzed by RT-PCR. β-Actin (α-β-actin) was detected as the loading control (top two panels). Total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with indicated antibodies (bottom six panels). B, B16F10 cells were transfected with vector or MC1R (mc1r). After serum starvation, the cells were activated using 10% FBS for 1 h. The phosphorylation of p38 was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-p38 (α-p-p38) antibody. p38 (α-p38) was detected as the loading control. C, B16F10 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting MC1R (si-mc1r). After serum starvation, the phosphorylation of p38 was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-p38 (α-p-p38) antibody. p38 (α-p38) was detected as the loading control (left panel). After serum starvation, the cells were activated using 10% FBS for 1 h and analyzed p38 activity by Western blotting (right penal). D, B16F10 cells were transfected with siRNA targeting MC1R (si-mc1r). B16F10 cells pretreated with SB239063 (5 μm, 30 min) were incubated for 24 h. mRNA expression of these cells was analyzed by RT-PCR (top panel), and the phosphorylation of p38 was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-specific p38 antibody (α-p-p38, middle panel). Cell migration was analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1 (bottom panel). *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.05 versus si-control.