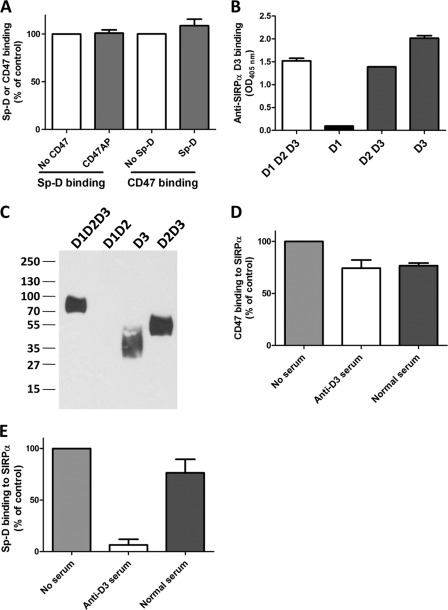
FIGURE 2.
Sp-D binding to SIRPα is not impaired by CD47 binding but is inhibited by an anti-human SIRPα D3 serum. A, in vitro binding assay showing that CD47 and Sp-D can both bind to SIRPα independently. Microtiter wells coated with SIRPα were first incubated with either recombinant ectodomain of CD47 or purified Sp-D, blocked, and then incubated with respective ligands to assess the binding of Sp-D (after incubation with CD47) or CD47 (after incubation with Sp-D). B, in vitro binding assay confirming anti-SIRPα D3 serum specificity for the D3 domain. Goat anti-rabbit IgG, γ-specific, was coated on microtiter plates, blocked, and subsequently incubated with rabbit Fc-tagged SIRPα WT or mutant proteins. Incubation with diluted anti-SIRPα D3 serum generated in BALB/c mice as detailed under “Materials and Methods” was followed by addition of peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. IgG binding was further determined by colorimetry using ABTS at 405 nm. C, Western blot of various SIRPα domains revealed with the mouse anti-human SIRPα D3 serum diluted 1:4000 followed by goat anti-mouse as described under “Materials and Methods.” D, CD47 binding to immobilized SIRPα D1D2D3 incubated with mouse normal and anti-D3 sera. Binding of CD47-AP was evaluated by colorimetry using p-nitrophenyl phosphate. E, Sp-D binding to immobilized SIRPα D1D2D3 incubated with normal and anti-D3 sera determined as indicated in Fig. 1B. Results are representative of one of three independent experiments. Error bars, S.E.