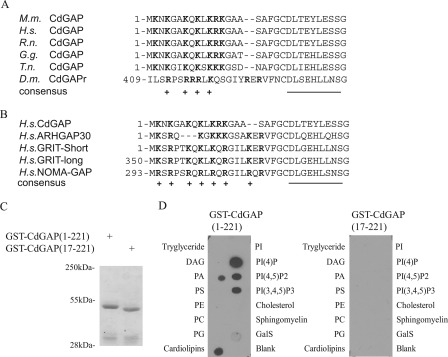
FIGURE 1.
A conserved PBR in CdGAP binds to phospholipids. Amino acid sequence alignment of the PBR in CdGAP from different species (A) and closest homologs (B). Positively charged amino acids are highlighted in bold and marked (+), whereas amino acids forming the first α-helix of the GAP domain are underlined. C, Coomassie Blue-stained gel showing recombinant purified glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged CdGAP(1–221) and CdGAP(17–221). D, lipid overlay assay of GST fusion proteins showing selective binding of GST-CdGAP(1–221), but not GST-CdGAP(17–221), to nitrocellulose-bound phosphoinositides. M.m., Mus musculus; H.s., Homo Sapiens; R.n., Rattus Norvegicus; G.g., Gallus gallus, T.n., tetraodon nigroviridis, D.m., Drosophila melanogaster. DAG, diacylglycerol; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PI(4)P, phosphatidylinositol (4)-phosphate; PI(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate; PI(3,4,5)P3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; GalS, 3-sulfogalactosylceramide.