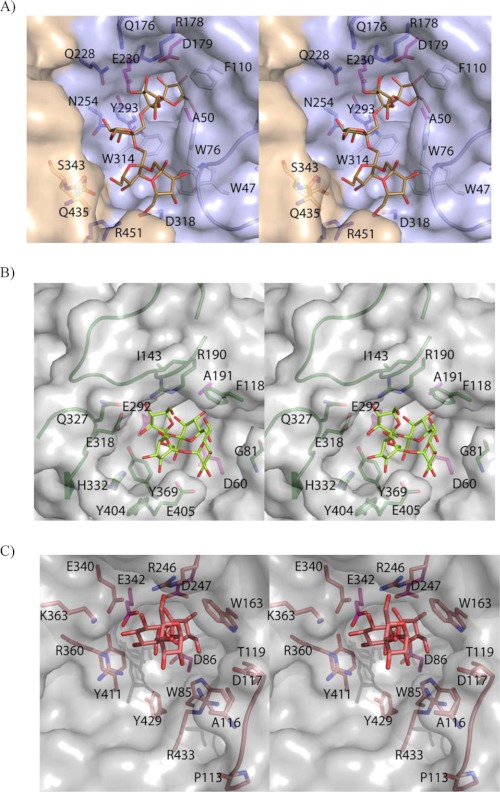
FIGURE 5.
Ffase active site specificity. A, stereo pair of the D50A-inulin complex with relevant residues highlighted. Only five fructose units that interact with Ffase are shown for clarity. Loop 70–80, absent in the A. japonicus FT, is in ribbon representation. Aromatic residues defining the hydrophobic wall of the active site are colored in white, and the three catalytic residues are pink. B, A. japonicus FT complexed with nystose (PDB code: 3LYH). Relevant residues are represented as sticks. Phe-118 is the unique hydrophobic residue present in the A. japonicus FT active site, with the fructose unit located at subsite +3 at an equivalent position to Ffase Trp-76. Two long insertions, absent in the known GH32 hydrolases, residues 140–153 and 320–331, are highlighted and hold Ile-143 and Gln-327, two residues proposed to provide a +2 subsite responsible for the formation of levan- or neo-type products. C, levansucrase from B. subtilis complexed with raffinose (PDB code: 3BYN). The Glu-340/Arg-360 pair, participating in subsites +1 and +2, is topologically and structurally equivalent to the Ffase Gln-228/Asn-254 pair. The interactions observed with the sugar at subsites +1 and +2 are conserved with levansucrases, and the different product specificities are proposed to be modulated by a distant loop that is represented in the figure.