Figure 4.
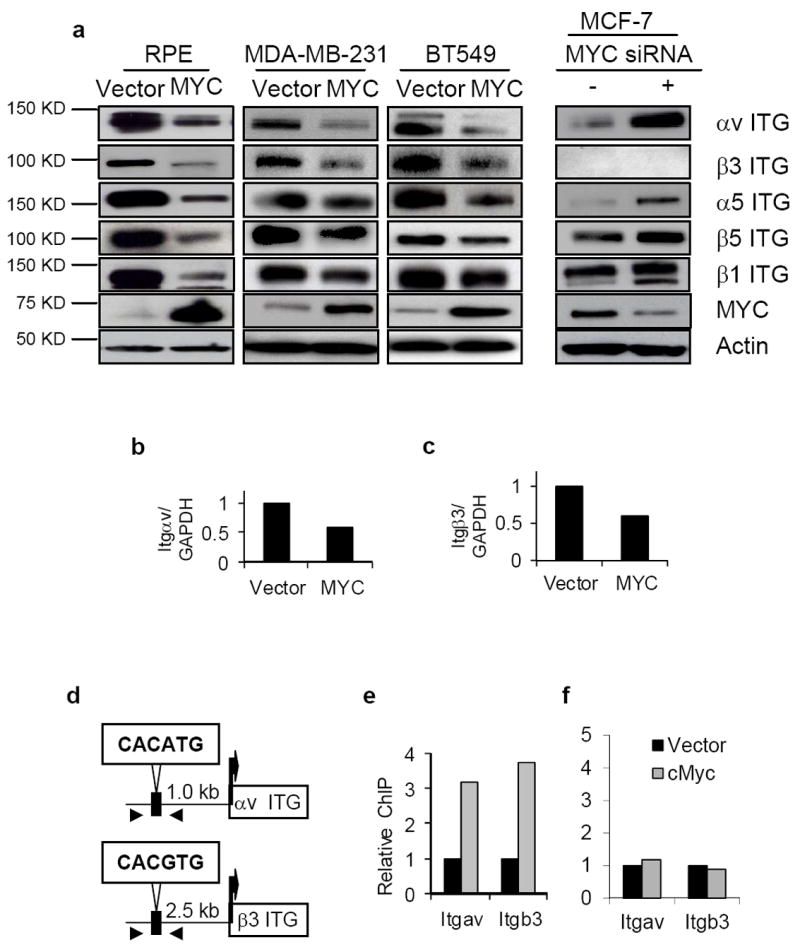
MYC down-regulates the expression of αv and β3 integrin genes through binding to their proximal promoters. (a) MYC modulates the abundance of αv and β3 integrins. Total lysates of the indicated cells were fractionated and immunoblotted with the antibodies against the integrins as shown. (b-c) Quantitative PCR assessment of integrin αv (Itgav; b) and β3 (Itgb3; c) expression in response to MYC expression in MDA-MB-231 cells (n=2 for each experiment). (d) Schematic illustration of the E-box motif upstream of αv and β3 integrin genes; arrowheads locate the designed primers for ChIP assay. (e-f) MYC binding to the proximal promoter of αv and β3 integrin genes as determined by ChIP assay. Cross-linked nuclear extracts of MDA-MB-231 transduced with vector only (black columns) or MYC (grey columns) were immunoprecipitated by either anti-MYC antibody or a control IgG. The regions of the MYC binding sites (e) or nonspecific sites (f) upstream of αv or β3 integrin genes were quantified and normalized to IgG pulldown (n=2 for each experiment). Data are expressed as mean± SEM. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.005.
