Figure 6.
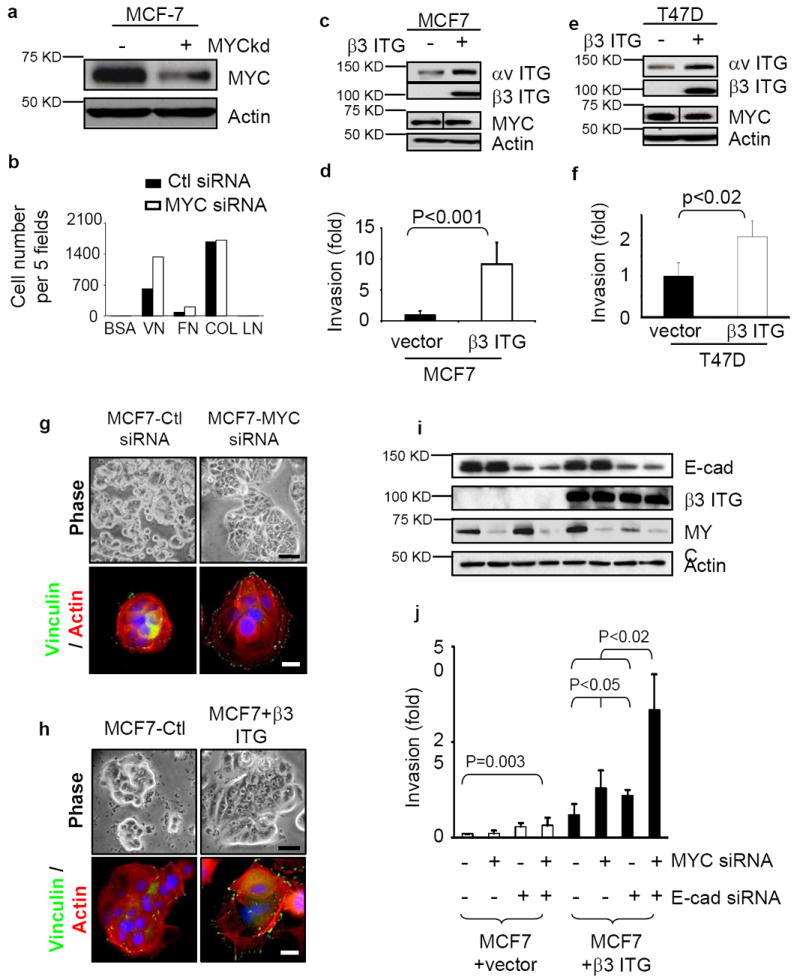
MYC and E-cadherin can prevent β3 integrin-induced invasion. (a) Suppression of MYC expression by siRNA in MCF7 cells assessed by western blot. (b) Suppression of MYC by siRNA augments cell adhesion to vitronectin and fibronectin. The cells in serum-free medium were plated into 96-well plates coated with purified matrix proteins (VN: vitronectin, FN: fibronectin, Col I: collagen I, LN: laminin). After 45 minutes, adhered cells were counted in five fields, n=2. (c-f) Ectopic expression of β3 integrin in MCF-7 (c) and T47D (e) cells, assessed by Western blot, enhanced invasiveness (d,f; n=3), as assessed by Boyden chamber assay. (g-h) Cell spreading, stress fiber and focal adhesion formation are enhanced in MCF7 cells when MYC is depleted by siRNA (g) or when β3 integrin is exogenously expressed (h). Changes in cell shape, actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesion formation were demonstrated by phase contrast (top) and staining with anti-vinculin (green) and Texas red Phalloidin (bottom). Scale bar: 20 μm for phase contrast and 5 μm for immunofluorescence staining. (i-j) Decreased expression of MYC and E-cadherin by siRNA increased the invasiveness of MCF7 cells only when β3 integrin was expressed. The depletion of MYC and E-cadherin was assessed by western blot (i) and invasiveness was assessed by Boyden chamber assays (j; n=3). Results are expressed as mean± SD.
