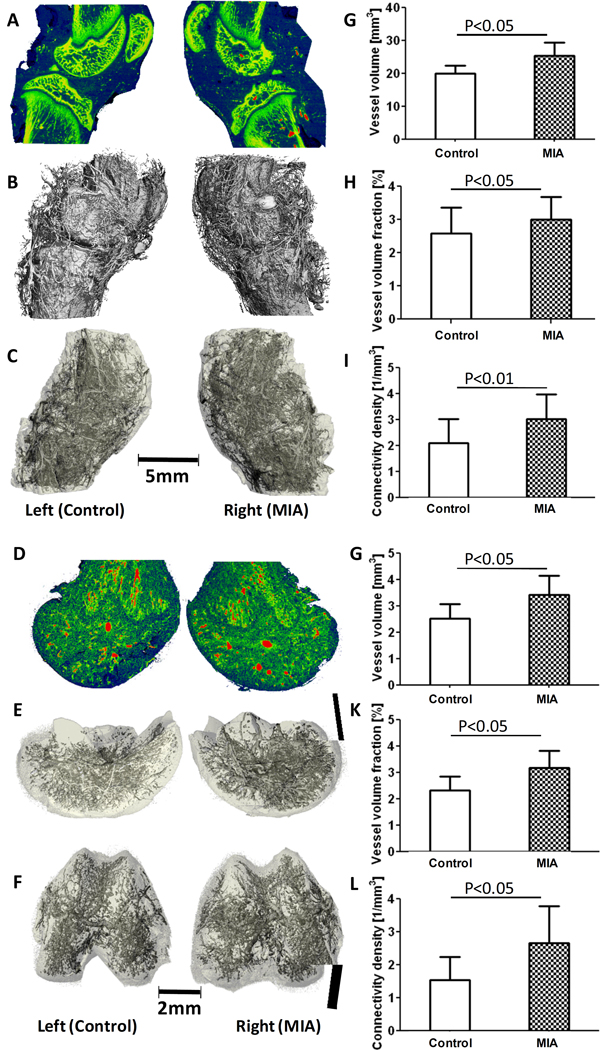
Figure 5.
Assessment of vascularization three weeks after MIA-injection to induce OA in rat knee joints. A: Representative sagittal section X-ray attenuation maps for MIA-induced and control joints, including bone and vasculature. Red represents the higher attenuating contrast-perfused vasculature, and green/yellow represents bone. B: Segmented µCT image including both bone and vasculature in the whole joints. C: Post-decalcification image depicting the full 3-D vascular network within and surrounding the joints. D: Sagittal section of X-ray attenuation maps for the decalcified distal femora. Red indicates higher attenuating main vasculature, and green indicates the smaller surrounding vessels. E: Segmented 3-D µCT image of vasculature within the distal femora (lateral view). F: Segmented 3-D µCT image of distal femora (distal condylar view). G-I: Results showed a significant increase in vascular volume (G), vascular volume fraction (H), and connectivity density (I) with MIA-injected joints vs. contralateral controls after 3 weeks. J-L: In the isolated distal femora, similarly to whole joint results, increases in vascular volume (J), vascular volume fraction (K), and connectivity density (L) were seen.