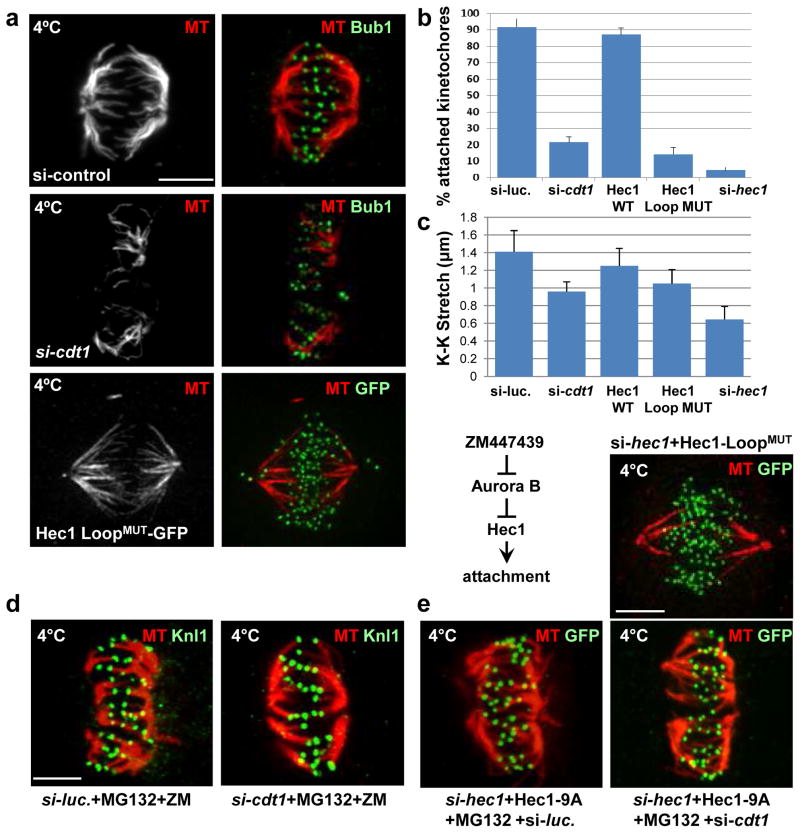
Figure 7. Cdt1 and the Hec1 Loopdomain are required for stable kMT attachments.
(a) Control cells in metaphase, Cdt1-depleted cells, and cells expressing Hec1 LoopMUT (in place of endogenous Hec1) in late prometaphase were incubated with ice-cold PBS (which allows retention of only stable kMTs) followed by fixation and staining with anti-tubulin antibody (MT) and either anti-Bub1 antibody to mark the kinetochores or anti-GFP antibody for ectopic Hec1 as indicated. (b) Quantification of the fraction of kinetochores making successful contact with K-fibers in Cdt1-depleted or Hec1 LoopMUT cells; n = 250 kinetochores (c) Inter-kinetochore (K-K) distances in the indicated cells; n = 100–125 kinetochores; p < 0.01. (d) Synchronized HeLa cells treated with either control luciferase or cdt1 siRNA as indicated were treated with both ZM447439 (Aurora B inhibitor) and MG132 (anaphase inhibitor) for hr at 8.5 hrs post-S phase release followed by cold treatment and staining with anti-tubulin antibody and anti-Knl1 antibody. (e) Synchronized HeLa cells were co-transfected with both hec1 siRNA and either a plasmid encoding unphosphorylatable 9A-Hec1- GFP (top panels) followed by MG132 treatment for hr at 8.5 hrs post S phase release or plasmid encoding Hec1 LoopMUT-GFP (bottom panel). The cells were then subjected to cold treatment at 9 hrs post-S phase release and stained with anti-tubulin antibody and anti-GFP antibody. Scale bars = 5 μm.