Figure 1.
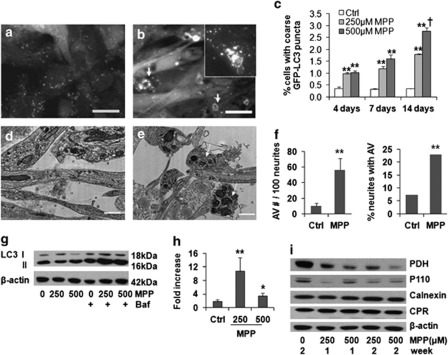
Selective mitophagy is induced in the 2-week MPP+ model. MPP+treatment (250 μM ) × 2 weeks induced formation of enlarged, coarse GFP-LC3 puncta, some displaying ring-like or bead-like morphology (b, arrows), compared with control (a). Autophagic puncta were also identified by immunostaining for endogenous LC3 (b, inset) (scale bar=20 μm). There were significant time- and dose-related increases in coarse GFP-LC3 puncta (c). **P<0.01 MPP+ versus Ctrl. †P<0.01 500 μM versus 250 μM. Electron microscopy revealed increased autolysosomal structures in neurites after MPP+ treatment (e) compared with control neurites (d) (scale bar=1 μm), quantified as increases in either the number of AVs in neurites or the number of neurites containing AVs (f) **P<0.01, MPP+ versus control, t-test, and chi-square test, respectively). Representative LC3 western blot shows increased LC3 II elicited by MPP+ in the presence of bafilomycin, added during the final 24 h to prevent degradation of newly formed AVs (g), and flux analysis using the change in LC3 II/actin ratios in the presence versus absence of bafilomycin confirmed a significant increase, particularly at the lower dose (h, n=3). **P<0.01, *P<0.05, MPP+versus Ctrl. Western blot showed mitochondrial protein loss (PDH, P110), with no change in endoplasmic reticulum proteins cytochrome p450 reductase (CPR) or calnexin (i)