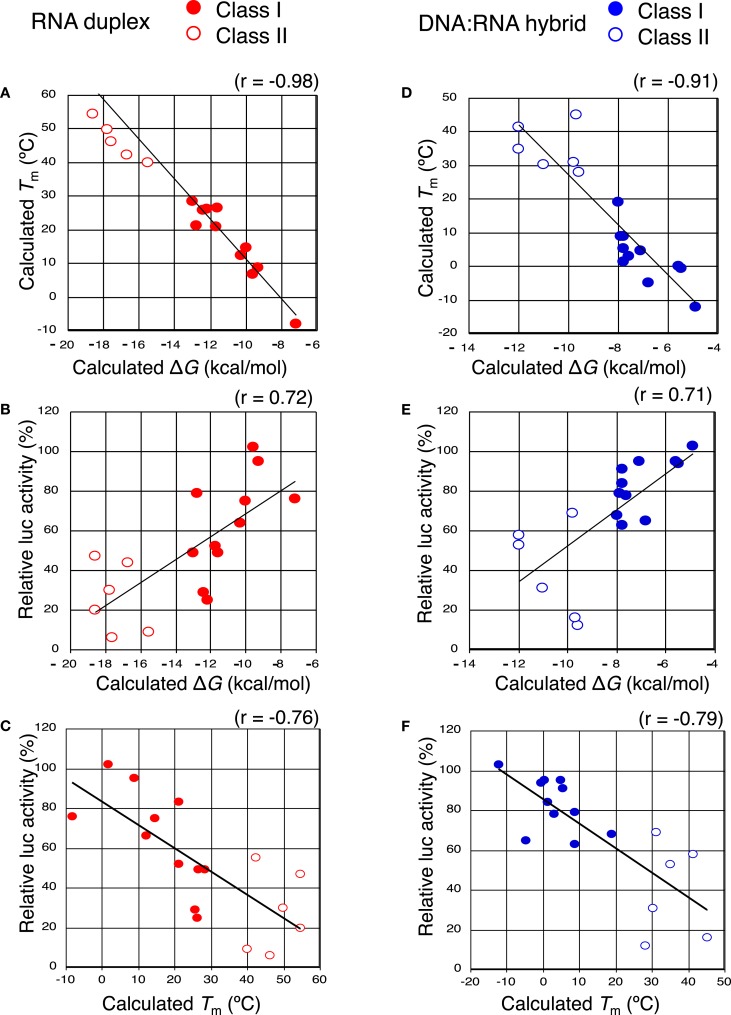
Figure 5.
The close relationship between the efficiency of seed-dependent off-target gene silencing and seed-target duplex thermodynamic stability. Both class I siRNAs and functional class II siRNAs (A–C) and class I chiRNAs and functional class II chiRNAs (D–F) were analyzed. Solid red circles and open red circles represent the class I and II siRNA data, respectively. Solid blue circles and open blue circles represent the class I and II chiRNA data, respectively. (A,D) The calculated Tm of the seed-target duplex decreased with increasing standard free energy (ΔG) for seed-target duplex formation (correlation coefficient: −0.98 and −0.91, respectively). (B,E) Luciferase activity (seed-dependent off-target gene silencing at a 50 nM siRNA concentration) was positively correlated with ΔG (correlation coefficient: 0.72 and 0.71, respectively). (C,F) The correlation between the seed-dependent gene silencing activity (luciferase activity) and the calculated Tm of the seed-target duplex. Luciferase activity based on seed-dependent gene silencing with 50 nM siRNA was obtained from Figures 4 and 7, respectively. Seed-target duplex ΔG and Tm were calculated using the nearest neighbor method. The relative luciferase activity and calculated Tm were correlated with each other and had a coefficient of −0.76 and −0.79, respectively.