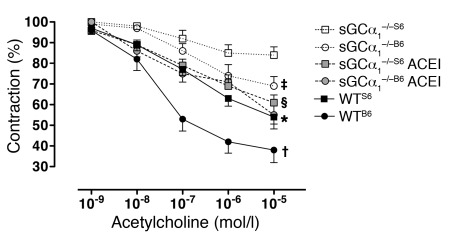
Figure 7. The strain-specific hypertension in sGCα1–/– mice is associated with greater impairment of vascular reactivity in sGCα1–/–S6 mice than in sGCα1–/–B6 mice.
Acetylcholine-induced relaxation was studied in phenylephrine-precontracted aortic rings from male wild-type (black symbols, solid line) and sGCα1-deficient mice (sGCα1–/–) on a B6 (circles) or S6 (squares) genetic background. sGCα1–/– mice were either pretreated (gray symbols, dashed line) or not (white symbols, dotted line) with the ACE inhibitor (ACEI) enalapril. Acetylcholine-induced vascular relaxation was impaired to a greater extent in sGCα1–/–S6 than in sGCα1–/–B6 mice. In vivo pretreatment with enalapril restored vascular reactivity in sGCα1–/–S6 to levels observed in sGCα1–/–B6 mice. n = 9, 8, 9, 4, 10, and 12 for sGCα1–/–S6, sGCα1–/–B6, sGCα1–/–S6ACEI, sGCα1–/–B6 ACEI, WTS6, and WTB6, respectively. *P < 0.001 versus sGCα1–/–S6; †P < 0.01 versus sGCα1–/–B6; ‡P < 0.05 versus sGCα1–/–S6; §P < 0.01 versus sGCα1–/–S6.