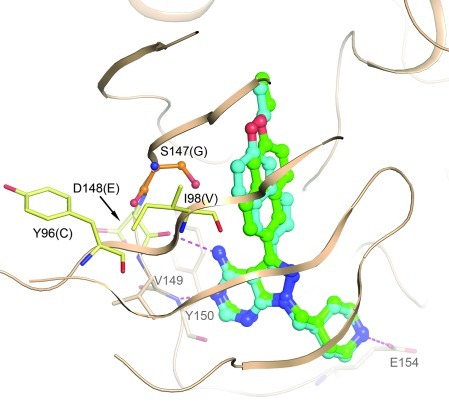
Figure 1. A homology model of PfCDPK4 was generated based on the crystal structure of the TgCDPK1:BKI-1 complex (PDB3sx9).
Modeling suggests 2 possible binding modes for BKI-1 in the active site of PfCDPK4, differing by the orientation of the “bump” in the “gatekeeper pocket,” but very similar to the binding modes seen in the crystal structure with TgCDPK1. Four residues within 8 Å of the bound BKI differ between PfCDPK4 and TgCDPK1. These are labeled in black, with the TgCDPK1 residue given in parentheses. Only the glycine/serine difference at the gatekeeper (orange sticks) is expected to have a significant influence on the binding mode of the inhibitor, as the other 3 (pale yellow sticks) contribute only backbone atoms to the pocket. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as magenta dashed lines. Conserved residues in the hinge region involved in binding and Glu154 are depicted as beige sticks and are labeled in gray.