Table 1.
Summary of primary prevention interventions targeting obesity prevention in the after school setting.
| # | Intervention | Theory | Intervention Duration & Description | Study | Design & sample | Salient findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Youth Fit For Life | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered in three 45-minute sessions over 12 weeks. -Program consisted of 4 components, targeting: (1) Cardiovascular exercise by noncompetitive games (2) Resistance exercise using resistance bands (3) Nutrition/health information (4) Behavioral skills training |
Annesi, 2006 [18] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 84 (2005) TX: n = 41 (2003) CNT: n = 40 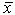 x age = 10.8 x age = 10.8 |
-Significant improvements for PA (p < 0.001), physical self-concept (p < 0.013) and self-efficacy for exercise barriers (p < 0.001) in the treatment group and no changes in the control. |
| Annesi, Faigenbaum, et al. 2008 [19] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 146 CNT: n = 123 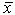 age = 10.6 age = 10.6 |
-Significant improvements for all self-appraisal factors (ex. general self (p < 0.003)), mood factors (ex. Tension (p < 0.001)) and PA (p < 0.001) within the treatment group. -Measures also significantly different between the TX and CNT groups at the time of posttest (p < 0.001). |
||||
| Annesi, Moore, et al. 2008 [20] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 217 Overall 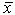 age = 9.7 age = 9.7 |
-Significant improvement for PA (p < 0.001) from baseline to the end of the program. -Significant negative predictors of PA post-intervention included frequency of PA at baseline (p < 0.001) and age (p < 0.007) |
||||
| Annesi, et al. 2009 [21] |
Pilot Study Total n = 43 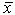 age = 9.0 years age = 9.0 years |
-Significant improvements found for BMI (p < 0.03), strength (p < 0.001), endurance (p < 0.04), engagement in PA (p < 0.01), vegetable intake (p < 0.02), self-efficacy for PA (p < 0.002) and physical self-concept (p < 0.05), but not flexibility, or fruit intake. | ||||
| Annesi, et al. 2011 [22] |
Quasi-Experimental TX :n = 121 TX plus HopSports® video-system: n = 171 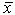 age = 7.3 years age = 7.3 years |
-Significant improvements for BMI-percentile (p < 0.001), muscular strength (p < 0.001), and cardio-respiratory endurance (p < 0.007) within both groups, but no difference between groups. | ||||
| 2. | Nutrition & Media Intervention | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered in 12 two-hour sessions over 6 weeks. -Program included education for nutrition, media literacy and health communication. |
Evans, et al. 2006 [23] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 18 CNT: n = 21 4th and 5th grade children |
-Significant improvements for motivation (p < 0.013), home nutrition environment (p < 0.02), and perceived parental support (p < 0.04), but not fruit/vegetable intake, self-support or self-efficacy. |
| 3. | Pilates Program | None stated | -Delivered every day for 4 weeks. -Program included basic training in Pilates. |
Jago, et al. 2006 [24] | Pilot Study TX: n = 16 CNT: n = 14 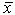 age = 11.2 years age = 11.2 years |
-Significant improvements for BMI-percentile (p < 0.039), but no other measure (ex. blood pressure) |
| 4. | 10-Month Physical Activity Intervention | None stated | -Delivered everyday school day for 110 minutes for a total of 10-months -For each session: 30 min. for homework; 25 min. PA skills development; 35 min. PA; and 20 min. toning/stretching |
Barbeau, et al. 2007 [25] |
RCT TX: n = 118 CNT: n = 83 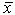 age = 9.5 years age = 9.5 years |
-Average attendance was 54% (2.5 days/week). -Significant improvements for BMI-percentile (p < 0.008), body composition (p < 0.0001), cardiovascular fitness (p < 0.047) and overall PA (p < 0.0006) were found for the treatment group, compared with the control group. |
| Howe, et al. 2011 [26] |
RCT TX: n = 62 CNT: n = 44 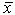 age = ~9.8 years age = ~9.8 years |
-Average attendance was 57.7% (2.5 days/week). -Significant improvements for children attending ≥60% of intervention for MVPA (p < 0.04), BMI (p < 0.0034), and body composition (p < 0.019) compared to the control group. |
||||
| 5. | Kids Living Fit | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered once per week for 12 weeks. -Sessions included various exercise and dietary components |
Speroni, et al. 2007 [27] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 80 CNT: n = 105 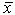 age ≈ 9.3 years age ≈ 9.3 years |
-Average attendance was 82%. -Children in TX group experienced a significant decrease in BMI-% (p < 0.01), while those in CNT group had a significant increase (p < 0.01). |
| 6. | Georgia Fitkid | None stated | -Delivered for 2 hours every school day for three-years. -For each session, 40 min. for eating a healthy snack and 80 min. for PA. |
Gutin, et al. 2008 [28] |
RCT TX: n = 148 CNT: n = 168 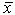 age = 8.5 years age = 8.5 years |
-Significant improvements for bone density (p < 0.01), fat-free soft tissue (p < 0.01), weight (p < 0.01), height (p < 0.01), and body mass index (p < 0.05) were found for TX group. -Also a group x time interaction for fitness (p < 0.01) and body fat % (p < 0.05) but benefits were not sustained during the summer. |
| 7. | Be a Fit Kid | Precede/ Proceed model | Delivered 3 times each week in 2 hours sessions for 12 weeks. -Program consisted of a PA, diet and parent component |
Slawta, et al. 2008 [29] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 75 6 to 12 years |
-Significant improvements for body composition (p < 0.001), fitness (p < 0.001), nutrition knowledge (p < 0.001), some dietary habits (ex. Total fat intake (p < 0.001), and for those who participated in at least 75% of the program, near significant reductions in total cholesterol (p < 0.059) and triglyceride levels (p < 0.099). |
| 8. | Food Fit | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered six 45-minute sessions over 6 weeks. -Program consisted of skills training to identify healthier foods. |
Branscum, et al. 2009 [30] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 58 3rd, 4th and 5th grade children |
-Significant improvements for overall dietary behaviors (p < 0.001), and behavior antecedents for some lessons. |
| 9. | Club Possible | Social Cognitive Theory | -Implementation varied by site. -Program consisted of education and behavior change activities for increasing PA, and improving healthy eating. |
Huberty, et al. 2009 [31] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 670 Age range: 5 to 11 |
-BMI-percentile significantly decreased among children (p < 0.0001). -There were no changes in PA self-efficacy, or social support among children ages 7−9 or 10−12, and only 7−9 age group significantly increased PA enjoyment (p < 0.002). |
| 10. | SCORES | None stated | -Delivered three 60-minute sessions weekly for 18 weeks. -A program that uses soccer to teach literacy in low-income areas. |
Madsen, et al. 2009 [32] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 178 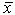 age = 9.7 years age = 9.7 years |
Overall physical fitness scores significantly increased (p < 0.001). No significant change was reported for overall BMI-percentile, except there was a significant decrease among Asian children (p < 0.001). |
| 11. | Ready. Set. ACTION! | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered fourteen 2-hour sessions and eight weekly booster session. -Incorporated theater activities with health promotion activities |
Neumark-Sztainer, et al. 2009 [33] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 51 CNT: n = 45 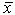 age = 10.3 years age = 10.3 years |
-No significant differences in changes for BMI-%, diet, PA, family/home environment or SCT constructs (except for self-efficacy for PA (p < 0.028)) |
| 12. | Tommie Smith Youth Athletic Initiative (TSYAI) | Trans-theoretical Model | -Delivered three 90-minute sessions/week for 14-weeks. -Included track & field and other PA games with various health promotion activities. |
Topp, et al. 2009 [34] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 63 K-5th grade children |
-Overall significant improvement for cardiovascular fitness (p < 0.01), but no change for BMI-% and percentage body fat. -Children also consumed significantly more green vegetables (p < 0.02) and less fruit juice (p < 0.02), but there were no other changes in diet. |
| 13. | HOP’N | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered over three years. -Contained daily PA (30-min.), healthy snacks, and weekly nutrition or PA educational experience. |
Dzewaltoski, et al. 2010 [35] |
RCT Tx: n = 134 Cnt: n = 112 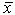 age = ~ 9.2 years age = ~ 9.2 years |
-No changes in BMI z-score observed. -Significant improvements found PA (p < 0.04) and sedentary behaviors (p < 0.01), especially among overweight/obese children. |
| 14. | Smart Snack | Social Cognitive Theory | -Program included three-90 min workshops implemented weekly. -Various program activities (ex. games) implemented to teach children healthy eating habits. |
Freedman, et al. 2010 [36] |
Pilot Study TX: n = 63 Age range: 9−14 years |
-Of various dietary measures milk (p < 0.05), vegetables (p < 0.05), and water intake (p < 0.05) significantly increased at posttest, but only water (p < 0.01) remained significant at the 3-month follow-up. |
| 15. | NutriActive | None stated | -Delivered everyday for 90-min, for 4-weeks. -Program included PA, snack and supervised non-structured play. |
Matvienko, et al. 2010 [37] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 42 CNT: n = 28 K and 1st grade children |
-Significant improvements for some fitness (ex. Push-ups (p < 0.001)) and all motor skill tests at 4 weeks (p < 0.001), however at the 4-month follow-up these improvements were no longer different between the TX and CNT group. |
| 16. | GEMS (Girls’ health Enrichment Multi-site Studies) | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered everyday for two hours, for 2-years. -Program consisted of teaching traditional and current dance, and strategies for reducing screen time. |
Robinson, et al. 2010 [38] |
RCT TX: n = 134 CNT: n = 127 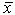 age = 9.4 years age = 9.4 years |
-No change for BMI in TX group, but reported significant improvements in cholesterol (p < 0.001), LDL (p < 0.001), and depressive symptoms (p < 0.02). |
| 17. | SNAP (Scouting Nutrition & Activity Program) | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered eight 60-90 minute sessions over four months. -Program consisted of: (1) An educational curriculum delivered by troop leaders; (2) Troop meeting policies; and (3) Badge assignments completed at home. |
Rosenkranz, et al. 2010 [39] |
RCT TX: n = 33 CNT: n = 39 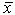 age = 10.6 years age = 10.6 years |
-Intervention troops significantly increased PA (p < 0.001) but no change for control troops. -No significant intervention effect on girl’s BMI z-scores, PA, fruit and vegetable consumption, or SSB consumption. -No significant intervention effect for parents FV consumption, PA, or SSB consumption. |
| 18. | Food and Fitness Fun Education Program (FFFEP) | None stated | -Delivered weekly for 30−60 minute sessions over sixteen weeks. -Program included lessons on healthy eating and physical activity and daily physical activities were implemented. |
Carson, et al. 2011 [40] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 1810 K-5th grade children |
-Significant improvements in nutrition (p < 0.01) and PA knowledge (p < 0.01) for TX group. -Parent surveys suggested that their child and own diet and PA behaviors changes as a result of the program. |
| 19. | LA Sprouts | None stated | -Delivered weekly for 90 minute sessions over twelve weeks. -Program included gardening, cooking and nutrition education. |
Davis, et al. 2011 [41] |
Quasi-Experimental TX: n = 34 CNT: n = 70 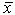 age = ~ 9.8 years age = ~ 9.8 years |
-Significant improvements for fiber (p < 0.04) and diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.04) for TX group, compared to CNT group. -For the overweight/obese sample, TX group significantly decreased BMI (p < 0.04) compared with CNT group. |
| 20. | Bienestar & CATCH | Social Cognitive Theory | -Delivered twice weekly for 65−90 minute sessions over twelve weeks. -Program included a bi-lingual health education program, and the PA component of CATCH. |
de Heer, et al. 2011 [42] |
RCT TX: n = 242 CNT: n = 326 Spillover: n = 236 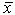 age = 9.2 years age = 9.2 years |
-Significant improvements for BMI-% (p < 0.045), aerobic capacity (p < 0.012) and intentions to eat healthy (p < 0.046) found for ASP’s that reported higher intervention exposure. |
