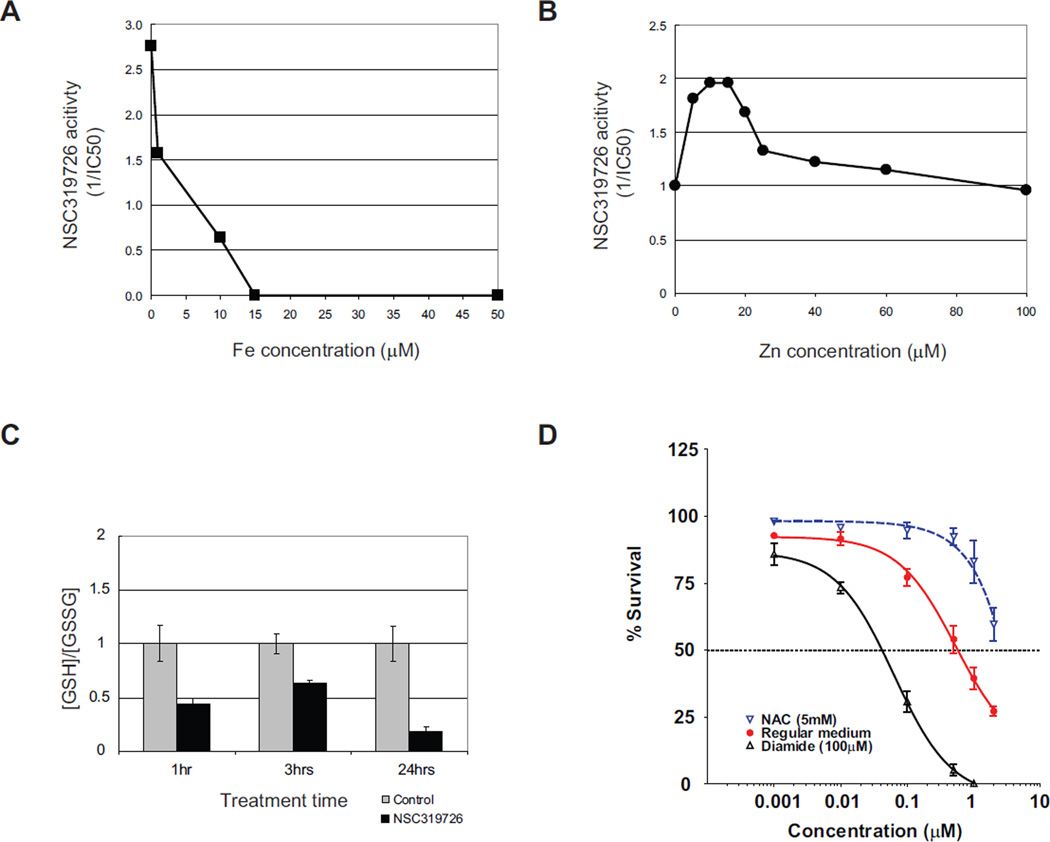
Figure 6. Zinc ion chelation and redox changes are important for the NSC319726 mediated p53-175 mutant reactivation.
(A) TOV112D cells are treated with NSC319726 with or without the presence of various concentrations of FeSO4, followed by measurement of growth inhibition. The NSC319726 activity is shown as 1/IC50 for cell growth inhibition. (B) TOV112D cells are treated with NSC319726 with or without addition of various concentrations of ZnCl2, followed by measurement of growth inhibition. The NSC319726 activity is shown as 1/IC50 for cell growth inhibition. (C) Ratio of reductant GSH and oxidative GSSG in the p53R175H cells upon NSC319726 (1 µM) treatment is measured at several time points (p=0.0057 at 1hr, p=0.0027 at 3hrs, and p=0.001 at 24hrs, t test). The error bars are +/− SD. (D) TOV112D cells are treated with NSC319726 using six serial dilutions (0.001 µM to 2 µM) with either N-acetyl cysteine (NAC, 5 mM) or diamide (100µM) for three days. The growth inhibition was analyzed by MTS assay as in Figure 1C. The error bars are +/− SD. See also Figure S2.