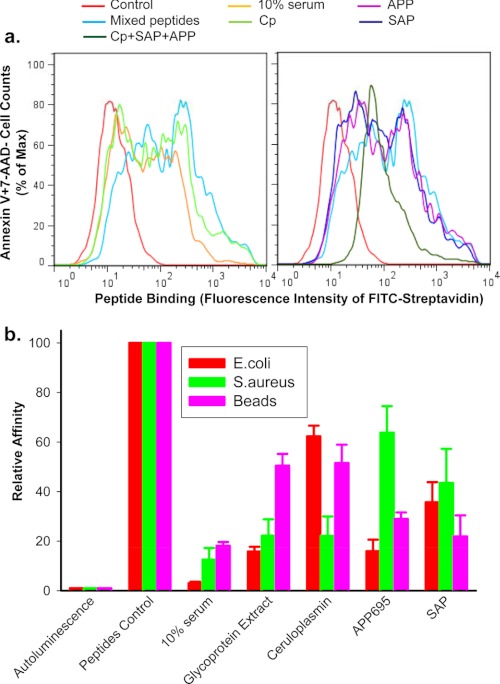
FIGURE 6.
Serum glycoproteins inhibit peptide binding to phagocytic target particles. Short biotin-labeled peptides, identical to the P2X7 extracellular domain sequence, show binding to the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes (a) or live E. coli, S. aureus, and 3-μm latex beads (b). Particles were incubated with mixed peptides (5 μg/ml each) in the presence or absence of 10% human serum, 0.5 mg/ml glycoprotein extract, 200 μg/ml purified CP, 200 μg/ml APP695, 100 μg/ml SAP for 15 min, or all three glycoproteins together. a, shown is a flow cytometry histogram of peptides binding. Apoptotic cells were incubated with FITC-conjugated streptavidin, APC-conjugated annexin V, and 7-AAD for 30 min. Cells were then analyzed by flow cytometry on gated Annexin V+7-AAD−/+ population. b, shown is peptide binding as measured by chemiluminescence assay. Beads and bacteria were incubation with 100 μl of HRP-labeled streptavidin (1:2000) for 15 min. Data were normalized to binding of peptide control in the absence of serum or glycoproteins and are presented as the mean ± S.D. (n = 3).