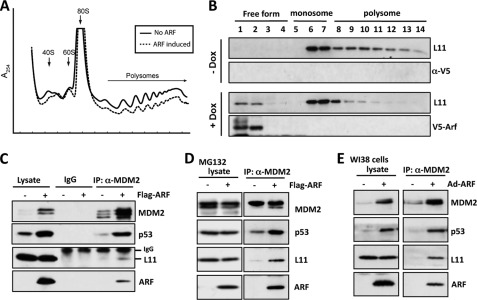
FIGURE 6.
ARF increases non-ribosome-associated form of L11 and the interaction of L11 with MDM2 and p53 in cells. A and B, ARF suppresses ribosomal biogenesis and increases non-ribosome-associated form of L11. Cytoplasmic extracts containing polysomes from U2OS-tet-V5-ARF cells cultured in the presence or absence of Dox for 48 h were subjected to a 15 to 47% linear sucrose gradient sedimentation centrifugation. After centrifugation, the distribution of polysomes and monosomes was measured by recording the absorbance of RNA at 254 nm using an in-line UV monitor in a Biocomp Gradient Station (A). Additionally, fourteen fractions were collected, and 30 μl of each fraction was subjected to IB with anti-L11 or anti-ARF antibodies as indicated. The fractions containing polysomes, monosomes, and ribosome-free forms of L11 are indicated on the top (B). C and D, overexpression of ARF enhanced endogenous L11-MDM2-p53 interaction in U2OS cells. Cells transfected with Flag-ARF or empty vector were untreated (C) or treated with 20 μm MG132 (D) for 8 h before harvest. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or anti-MDM2 (SMP14 and 4B11), followed by IB with polyclonal anti-p53, anti-MDM2 (2A10), anti-ARF, or anti-L11 antibodies, as indicated. E, overexpression of ARF enhanced endogenous L11-MDM2-p53 interaction in WI38 cells. Cells infected with Ad-ARF or control viruses were subjected to co-IP using anti-MDM2 (SMP14), followed by IB with polyclonal anti-p53, anti-MDM2 (2A10), anti-ARF, or anti-L11 antibodies.