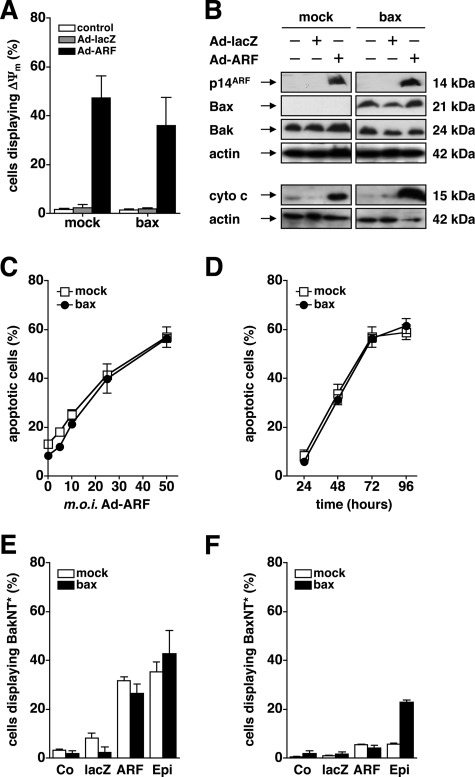
FIGURE 1.
P14ARF-induced cell death is Bax-independent and coincides with activation of Bak. A, p53-mutated, Bax-deficient (mock) or Bax-reconstituted (bax) DU145 cells were infected with the indicated adenoviral vectors at an m.o.i. of 50 or mock-treated for 48 h. Loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) was determined by flow-cytometry using the cationic dye 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethyl-benzimidazolylcarbocyanin iodide. The relative number of cells displaying ΔΨm is given. B, DU145 cells were infected with the indicated adenoviral vectors (50 m.o.i.) or mock-treated. Total cellular proteins (25 μg/lane) were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blot analysis using the indicated antibodies. C and D, cells were infected with Ad-p14ARF or mock-treated for 72 h. Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometric detection of fragmented nuclear DNA. Cells displaying a sub-G1 DNA content were less than 10% upon infection with an Ad-lacZ control adenovirus (50 m.o.i., data not shown). E and F, DU145 cells were infected with Ad-ARF or Ad-lacZ (50 m.o.i.) or mock-treated (Co) for 48 h. In parallel, cells were exposed to epirubicine (Epi, 1 μg/μl) as a positive control. An N-terminal conformational change of Bax (BaxNT*) (E) or Bak (BakNT*) (F) was studied by flow cytometry using conformation-specific antibodies. Error bars represent mean ± S.D. from triplicates.