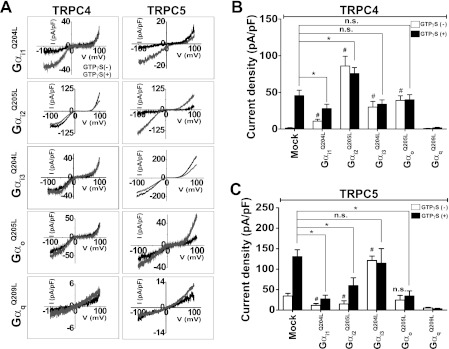
FIGURE 2.
Effect of Gα isoforms on TPRC4 and TRPC5 activity. A, representative I-V relationships of TRPC4 and TRPC5 show the effect of constitutively active Gα QL mutants on the electrophysiological properties of the TRPC4 and TRPC5 channels. B, summary of TRPC4 current density activation by Gα subunits and/or by GTPγS. Note the variable effects of the Gα mutants. All Gα mutants activate TRPC4 channels without an activator (e.g. GTPγS or carbachol (CCh)). Gαi2 provided the most effective activation of TRPC4, whereas Gαq inhibited TRPC4. Current density is represented by maximal current peaks (subtracted Cs+ basal current) at −60 mV in Cs+ solution and is indicated by means ± S.E. Statistical significance was denoted by an asterisk (open column) and number sign (closed column) at p < 0.05. C, summary of TRPC5 activation by Gα subtypes showing that the most effective activator is Gαi3 and that most Gα mutants inhibit the TRPC5 channel, with Gαq inhibiting TRPC5. Current density was obtained by the methods described above. Statistical significance was denoted by an asterisk (open column) and number sign (closed column) at p < 0.05. n. s., not significant.