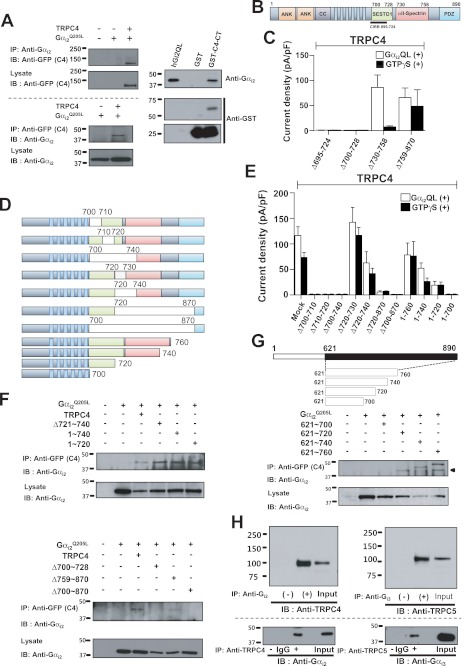
FIGURE 5.
Interaction of Gαi2 with the C terminus of TRPC4. A, TRPC4 co-immunoprecipitates with Gαi2. HEK cells were transfected with empty vector, Gαi2 alone, and Gαi2 with TRPC4-GFP and were used to test reciprocal co-IP of TRPC4 and Gαi2. TRPC4 C-terminal GST fusion protein was used to probe direct binding between Gαi2 and TRPC4. Binding of the TRPC4 C-terminal GST fusion protein with recombinant human Gαi2Q205L protein was shown by Gαi2-antibody in vitro binding assay. B, a schematic of GFP-fused TRPC4. C, summary of the effects of Gαi2 on TRPC4 C-terminal truncation mutants in the presence and absence of GTPγS stimulation. Current densities are represented by subtracted maximal maximal current peaks at −60 mV in Cs+ solution and are indicated by means ± S.E. D, schematic of GFP-fused TRPC4 deletion and truncation mutants used (upper panel). Wild-type TRPC4 and mutants were probed using the GFP antibody in immunoblotting (bottom). E, summary of the effects of Gαi2 on current by TRPC4 deletion and truncation mutants in the presence and absence of GTPγS stimulation. Current density was obtained by the methods described above. F, interaction between Gαi2, TRPC4, and mutants was tested by co-IP, and the interaction site was mapped to the 700∼728 region (the SESTD1 domain of TRPC4β). G, a schematic of GFP-fused C-terminal fragments of TRPC4 (upper panel) and their co-IP with Gαi2. H, the association between Gαi with TRPC4/5 in vivo. Gαi2 and Gαi3 were immunoprecipitated from rat brain extract and were probed for TRPC4 and TRPC5 to show co-IP in vivo (upper panel). TRPC4 and TRPC5 were co-immunoprecipitated reciprocally. Lanes of IgG and control (−) did not show Gαi binding. Input was indicated as 10% input of brain extract. IB, immunoblot.