FIGURE 5.
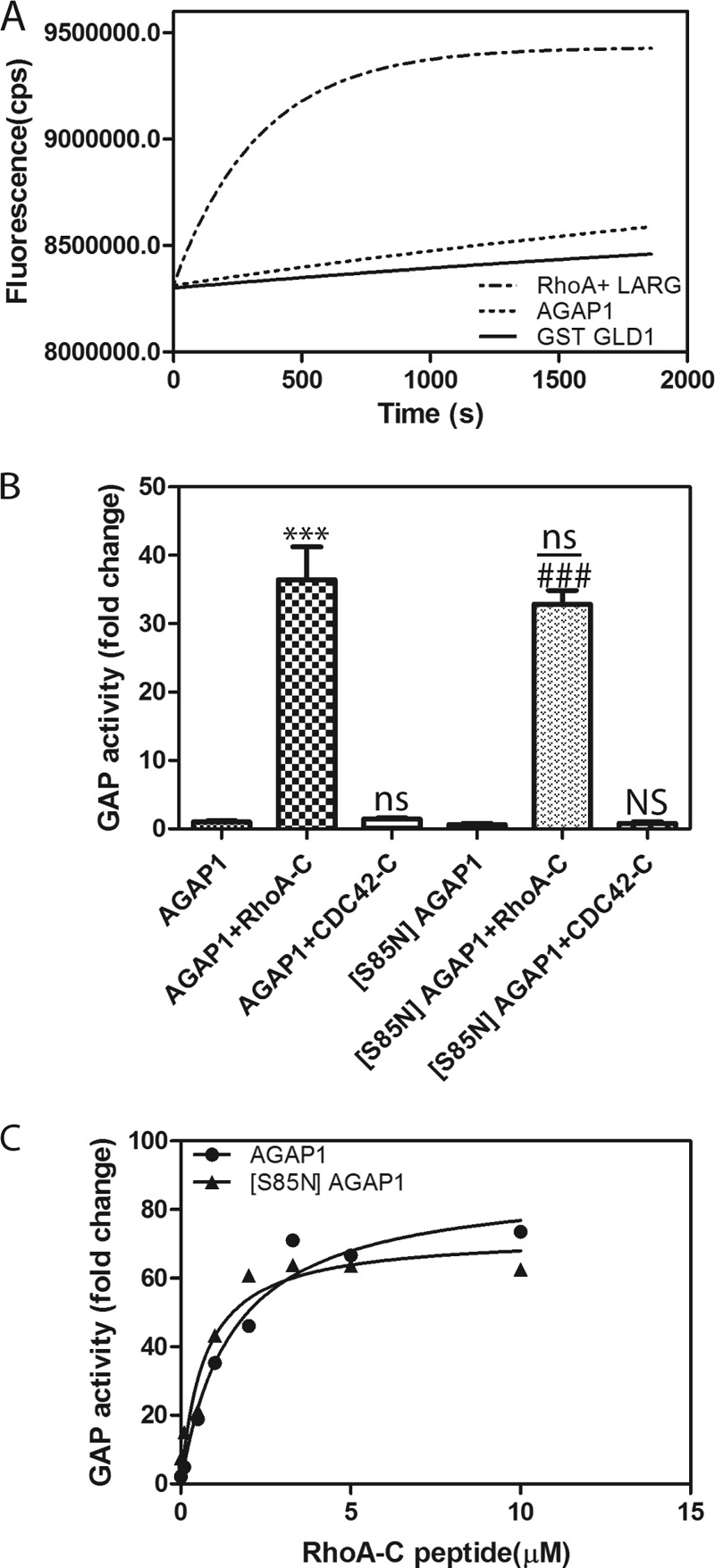
Tests for role for nucleotide binding to AGAP1. A, no association with BODIPY-GTPγS detected. Nucleotide binding was measured by incubating 0.5 μm his10AGAP1 or GST-GLD with 17.5 nm BODIPY-GTPγS in a buffer containing 20 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mm NaCl, 2 mm DTT, 1 mm EDTA, 0.5 mm MgCl2. Binding to RhoA catalyzed by LARG DH/PH is shown as a positive control. The reaction contained 2.5 μm RhoA, 200 nm leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (LARG), and 17.5 nm BODIPY-GTPγS in a reaction mixture that was the same as for the AGAPs except 3 mm MgCl2 was present. B, P-loop mutation had no effect on activity. GAP activity of His10AGAP1 and His10 [S85N]AGAP1 was compared in reactions containing 1.1 nm concentrations of the indicated recombinant AGAP1 and, where indicated, 10 μm RhoA C-terminal peptide or Cdc42 C-terminal peptide. The data were analyzed by one way analysis of variance followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison test. ***, p < 0.001 compared with AGAP1 alone; ns, not significantly different than AGAP1 alone; ###, p < 0.001 compared with [S85N]AGAP1 alone; NS, not significant compared with [S85N]AGAP1 alone; ns, not significant compared with AGAP1 + RhoA-C. C, titration of RhoA-C peptide into reaction with His-AGAP1 and His-[S85N]AGAP1 is shown. GAP activity was determined using a fixed time point assay, and reaction mixtures contained 1.1 nm AGAP1 or 1.1 nm [S85N]AGAP1 and 0.2 μm [α32P]GTP·Arf1 as the substrate and the indicated concentration of peptides from either the C terminus of RhoA (RhoA-C) or Cdc42 (Cdc42-C).
