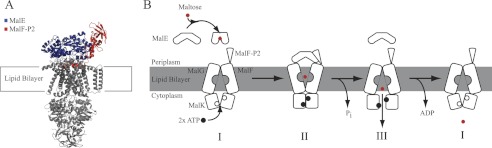
FIGURE 1.
Substrate transport model for MalFGK2-E. A, crystal structures of MalFGK2-E (6), MalE, and MalF-P2 color-coded in blue and red, respectively. B, transport model for ABC importer systems adapted to the MalFGK2-E system (10). The model contains three distinct steps. First, ATP is loaded into the MalK dimer, and the interface closes upon binding of substrate-loaded MalE at the periplasmic surface (II). Upon ATP hydrolysis substrate is released into the binding pocket of MalG,F and is transported into the cytoplasm (III). After substrate transport, ADP is released, and the transporter goes back to its resting-state (I). Amplitudes of motion for the TMDs are exaggerated in the representation to highlight changes. A TMD (MalF,G) rotation from the inward to the outward conformation was determined to be on the order of 22 ° (4). Fig. adapted from Locher (10).