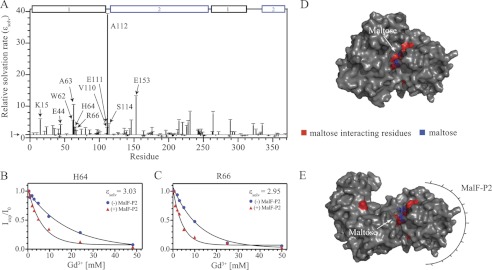
FIGURE 6.
Residue-specific solvent accessibility of MalE in the absence and presence of MalF-P2. A, relative solvent accessibility rates ϵsolv determined by solvent-PRE measurements. Conformational changes due to the complex formation of MalE/MalF-P2/maltose induce small changes of solvation rates over the full primary sequence. Residues in the vicinity of the maltose-binding pocket (marked with arrows) show similar or significantly higher solvation ratios in the presence of MalF-P2. B and C, relaxation rates for residues His64 and Arg66, interacting directly with maltose, in the absence (blue spheres) and presence (red triangles) of MalF-P2, respectively. D and E, surface representations of the MalE/maltose structures in the absence (PDB ID code 1MPD) and presence of MalF-P2 (Module-derived), respectively. Maltose (blue stick model) and interacting residues (red) are labeled in the structures.