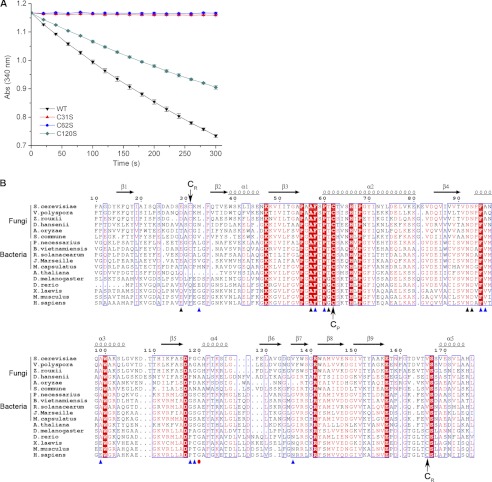
FIGURE 1.
Assignment of the CP and CR of Ahp1. A, shown are peroxidase activity assays. Assays were performed with Ahp1 (black inverted triangles), Ahp1C31S (red triangles), Ahp1C62S (blue circles), and Ahp1C120S (dark cyan diamonds). B, shown is multiple-sequence alignment of Ahp1 against other Prx5 subfamily proteins from different organisms. Both Cys-62 and Cys-31 of Ahp1 are conserved through homologs from several species of fungi and bacteria. In contrast, the homologs from several species of higher eukaryotes lack the corresponding resolving Cys-31 (CR) and have a conserved resolving CR at the C-terminal region. The multi-sequence alignment was performed using programs MultAlin (52) and ESPrint (53). The secondary structural elements of reduced Ahp1 are displayed above the sequences. The residues contributed to dimer interface were indicated with black (hydrogen bonds) and blue (hydrophobic interactions) triangles. Cys-120 was indicated with a red dot. All sequences were downloaded from the NCBI data base (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The sequences are (NCBI accession numbers codes are in parentheses) S. cerevisiae Ahp1 (NP_013210.1), Vanderwaltozyma polyspora Kpol_1004p59 (XP_001645540.1), Zygosaccharomyces rouxii ZYRO0D06248p (XP_002496705.1), Debaryomyces hansenii DEHA2G17864p (XP_462316.1), Aspergillus oryzae pmp20 (XP_001727651.1), Schizophyllum commune SCHCODRAFT_67750 (XP_003031587.1), Polynucleobacter necessarius redoxin domain-containing protein (YP_001154958.1), Ralstonia solanacearum peroxiredoxin (YP_003744570.1), Methylococcus capsulatus anti-oxidant AhpC-TSA family protein (YP_112582.1), Burkholderia vietnamiensis redoxin domain-containing protein (YP_001118388.1), Janthinobacterium Marseille peroxiredoxin (YP_001354699.1), Arabidopsis thaliana Prx-2D (NP_564763.1), Drosophila melanogaster peroxiredoxin 5 (NP_001027191.1), Danio rerio Prx 5 (NP_001019577.1), Xenopus laevis Prx 5 (NP_001085580.1), Mus musculus Prx 5 (NP_036151.1), and Homo sapiens Prx 5 (NP_036226.1).