FIGURE 1.
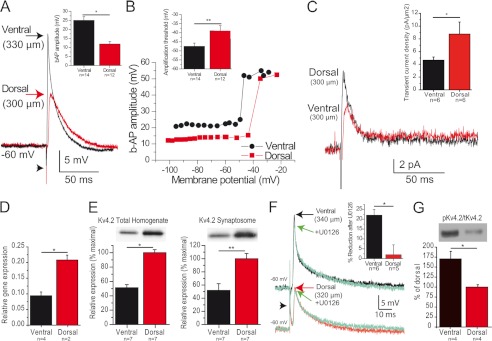
Backpropagation is enhanced in ventral hippocampus. A, example of b-APs recorded in CA1 pyramidal cell distal dendrites from the ventral (black) and dorsal (red) hippocampus. The arrowhead indicates the stimulus artifact. Inset, summary of b-AP amplitude in dorsal and ventral hippocampus. B, variation of the amplitude of b-APs as a function of membrane potential (same dendrites as in A). Note the sharp amplification marking the transition threshold. Inset, summary of transition threshold potential in dorsal and ventral hippocampus. C, dendritic cell-attached recordings reveal a larger amplitude of the transient A-type current in dorsal versus ventral cells (measured at +55 mV), whereas the amplitude of the sustained K+ current appears similar. Inset, summary of current density of A-type current in dorsal and ventral hippocampus. D and E, Kv4.2 expression is twice larger in the dorsal than in the ventral part of the hippocampus at the mRNA (D), total protein (E, left panel), and synaptosome protein (E, right panel) levels. F, the MEK inhibitor U0126 significantly reduced b-AP amplitude in ventral but not dorsal dendrites. G, the ERK-dependent phosphorylation of Kv4.2 was larger in the ventral than in the dorsal hippocampus. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.