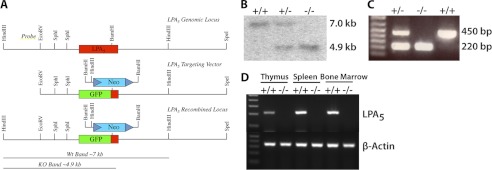
FIGURE 1.
Targeted disruption of the Lpar5 genomic locus and generation of LPA5-deficient mice by homologous recombination. A, schematic diagram of the Lpar5 gene targeting strategy. To generate the Lpar5 targeting vector, a portion of the Lpar5 coding region was removed and replaced in frame by enhanced GFP (middle panel). ES cell clones positive for homologous recombination were identified by digestion of genomic DNA with HindIII and Southern blotting with the external probe shown in the top panel. ES cell clones with nonhomologous recombination events showed a 7-kb band, whereas clones with homologously recombined DNA produced a 4.9-kb band. B, Southern blot showing the properly recombined product for a wild type (7 kb), heterozygous, and homozygous animal (4.9 kb). C, PCR genotyping showing the Lpar5 wild type (450 bp) and mutant (220 bp) products, primers are indicated in A. D, RT-PCR of cDNA from thymus, spleen, and bone marrow from wild type and Lpar5 homozygous mutant mice shows an absence of Lpar5 mRNA in tissues from LPA5-deficient animals. β-Actin control for all tissues is shown.