FIGURE 5.
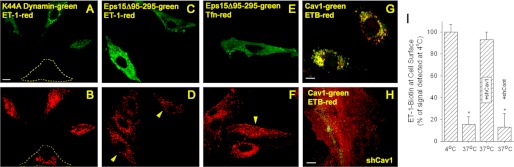
Role of dynamin and caveolin-1 but not Eps15 in rapid internalization of ET-1 and ET-B in cultured endothelial cells. A–F, images from confocal fluorescence microscopy of intact BAEC expressing either K44A Dynamin2-eGFP (green) (A and B) or Eps15-eGFP mutant (green) (C–F), and localization of either tetramethylrhodamine-ET1 (red) (A–D) or tetramethylrhodamine-Tfn (red) (E and F) after binding at 4 °C followed by warming to 37 °C for 5 min prior to fixation with paraformaldehyde (see “Experimental Procedures”). The dashed lines in A and B outline the positions of untransfected cell. The arrowheads in D and F denote Eps15 mutant transfected cells. G and H, localization of cav1 and ETB after 5 min of stimulation with ET1 of BAEC that were uninfected (G) or already infected for 24 h with shCav1 (H). I, histogram showing relative biotinylated ET-1 cell surface signal detected using an enzyme-linked, avidin-based detection assay (see “Experimental Procedures”). Intact, nonfixed BAEC were incubated with biotinylated ET-1 at 4 °C. Some cells (labeled 4 °C) were immediately fixed and processed for biotin detection. The other cells (labeled 37 °C) were first warmed to 37 °C for 5 min before processing. The cells infected for 24 h with shRNA lentivirus transduction particle are indicated as either +shCav1 for caveolin-1 shRNA or with control shRNA lentivirus transduction particle (+shCont) for control shRNA. *, p < 0.05 (analysis of variance/Tukey's range test). n ≥ 3 experiments of triplicate wells for each experiment. The bar represents 50 μm.