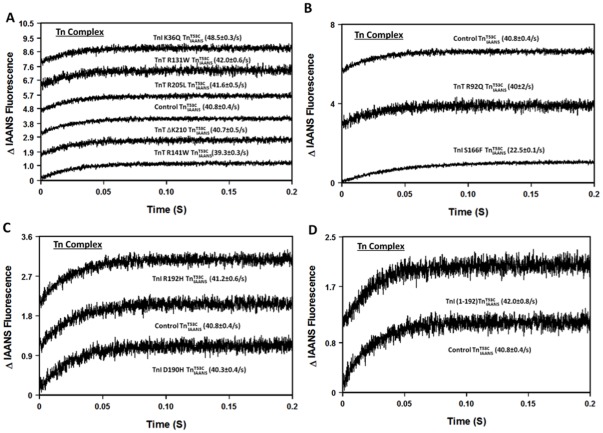
Figure 2. Effect of disease-related protein modifications on the rate of Ca2+ dissociation from the Tn complex.
Panel A shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control 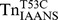 , and the DCM mutants, TnI K36Q
, and the DCM mutants, TnI K36Q 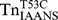 , TnT R131W
, TnT R131W 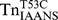 , TnT R141W
, TnT R141W 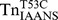 , TnT R205L
, TnT R205L 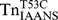 and TnT ΔK210
and TnT ΔK210 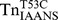 . Panel B shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control
. Panel B shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control 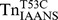 , and the HCM mutants, TnT R92Q
, and the HCM mutants, TnT R92Q 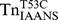 and TnI S166F
and TnI S166F 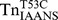 . Panel C shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control
. Panel C shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control 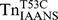 , and the RCM mutants, TnI D190H
, and the RCM mutants, TnI D190H 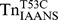 and TnI R192H
and TnI R192H 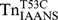 . Panel D shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control
. Panel D shows the time courses of the increase in IAANS fluorescence as Ca2+ was removed by EGTA from control 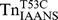 and ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192)
and ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192) 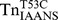 . All
. All 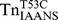 complexes consist of the full length Tn subunits of
complexes consist of the full length Tn subunits of 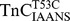 , TnI and TnT, except for ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192). The disease related modification is either in TnI or TnT, in either case, the other protein (TnT or TnI) was wild type. Data traces (an average of 3 to 5 individual traces collected at least 10 times) were fit with a single exponential equation to calculate the kinetic rates. The data traces have been staggered and normalized for clarity.
, TnI and TnT, except for ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192). The disease related modification is either in TnI or TnT, in either case, the other protein (TnT or TnI) was wild type. Data traces (an average of 3 to 5 individual traces collected at least 10 times) were fit with a single exponential equation to calculate the kinetic rates. The data traces have been staggered and normalized for clarity.