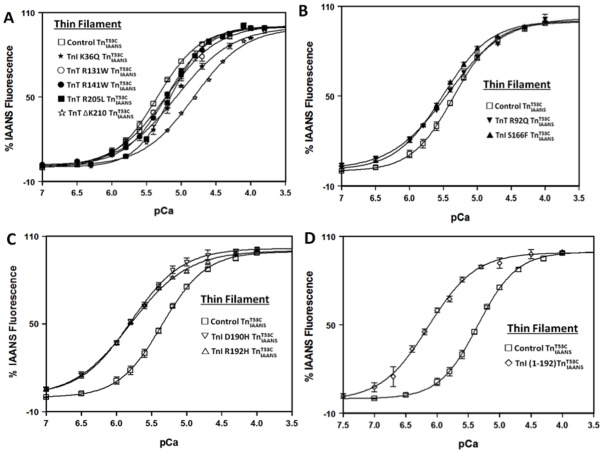
Figure 3. Effect of disease-related protein modifications on the Ca2+ binding sensitivity of the thin filament.
Panel A shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control 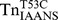 (□), and the DCM mutants, TnI K36Q
(□), and the DCM mutants, TnI K36Q 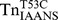 (
( ), TnT R131W (○)
), TnT R131W (○)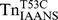 , TnT R141W
, TnT R141W 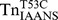 (•), TnT R205L
(•), TnT R205L 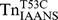 (▪) and TnT ΔK210
(▪) and TnT ΔK210 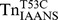 (⋆) as a function of pCa. Panel B shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control
(⋆) as a function of pCa. Panel B shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control 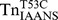 (□), and the HCM mutants, TnT R92Q
(□), and the HCM mutants, TnT R92Q 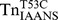 (▾) and TnI S166F
(▾) and TnI S166F 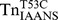 (▴) as a function of pCa. Panel C shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control
(▴) as a function of pCa. Panel C shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control 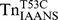 (□), and the RCM mutants, TnI D190H
(□), and the RCM mutants, TnI D190H 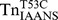 (▽) and TnI R192H
(▽) and TnI R192H 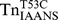 (▵) as a function of pCa. Panel D shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control
(▵) as a function of pCa. Panel D shows the Ca2+ dependent increases in IAANS fluorescence for thin filament bound control 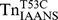 (□) and ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192)
(□) and ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192) 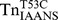 (
(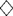 ) as a function of pCa. The data sets were normalized individually for each mutant. All
) as a function of pCa. The data sets were normalized individually for each mutant. All 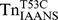 complexes consist of the full length Tn subunits of
complexes consist of the full length Tn subunits of 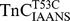 , TnI and TnT, except for ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192). The disease related modification is either in TnI or TnT, in either case, the other protein (TnT or TnI) was wild type. The Ca2+ sensitivities were reported as a dissociation constant Kd, representing a mean of three to four separate titrations ± S.E.M.
, TnI and TnT, except for ischemic related truncated TnI (1-192). The disease related modification is either in TnI or TnT, in either case, the other protein (TnT or TnI) was wild type. The Ca2+ sensitivities were reported as a dissociation constant Kd, representing a mean of three to four separate titrations ± S.E.M.