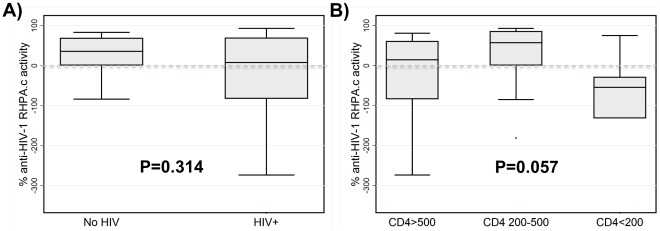
Figure 3. Inhibition by cervicovaginal lavage of T/F virus RPHA.c derived from a woman who reported heterosexual intercourse as her risk for contracting HIV.
(A) There was no statistically significant difference between median values of inhibition of RPHA.c comparing women with and without HIV infection. (B) Among HIV-infected women, HIV disease progression stage modulated the inhibitory effect of cervicovaginal lavage fluid on RPHA.c. Negative anti-HIV activity values indicate enhancement of infection. Bars depict median, interquartile range and 95% confidence intervals; P values via (A) Mann-Whitney U test and (B) Kruskal-Wallis test.