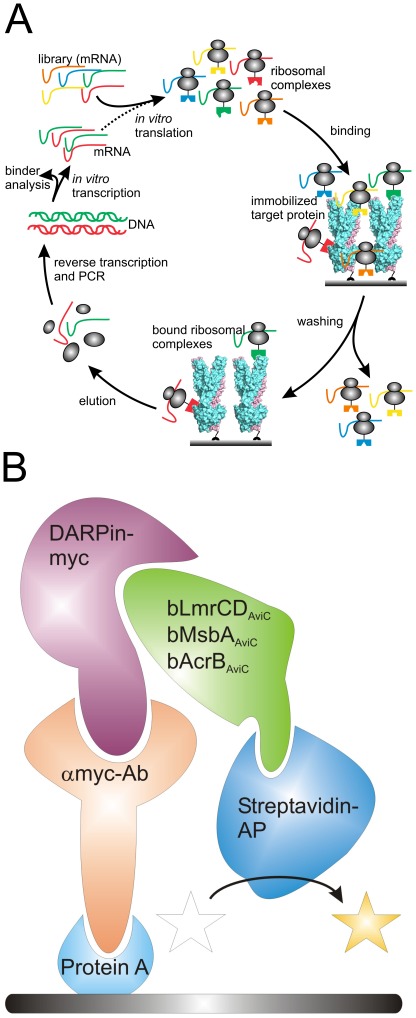
Figure 1. Ribosome display and ELISA set-up.
(A) Sketch delineating one DARPin selection round using ribosome display (adopted from [31]). The DARPin library in form of mRNA is in vitro translated and stable ribosomal complexes linking the phenotype (folded DARPins) with the genotype (translated mRNA) are generated. The ribosomal complexes are allowed to bind to immobilized bLmrCDAviC. After a washing step of variable length (depending on selection stringency), bound ribosomal complexes are destabilized and mRNA encoding for potential target-specific DARPins is liberated. The eluted mRNA is amplified by reverse transcription and PCR to double stranded DNA, which is in vitro transcribed into mRNA for another round of selection or used for binder analysis. (B) Schematic drawing of the ELISA set up. Protein A is coated onto the ELISA well and is decorated with an anti-myc antibody that immobilizes the DARPins via the C-terminal Myc5-tag. Upon binding of purified, biotinylated target protein (e.g. LmrCD, AcrB or MsbA in our study) to DARPin, the target protein is detected using a streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase the activity of which was detected colourimetrically at OD405 using p-nitrophenyl phosphate as a substrate.