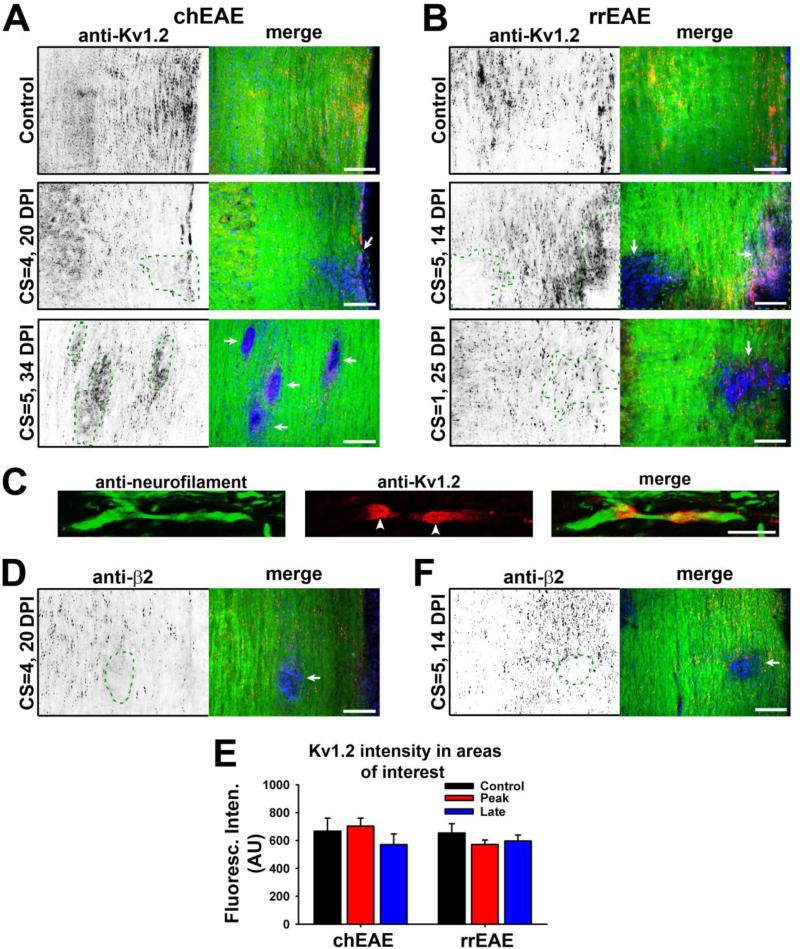
Figure 2. Alterations of Kv1.2/Kvβ2 JXP targeting within lesion areas in EAE spinal cord.
(A) Kv1.2 JXP clustering in myelinated axons of spinal cord white matter was altered in chEAE lesions. Kv1.2 staining signals are inverted (left) and are in red in the merged image (right). In merged images, FMG staining is in green and nuclear staining in blue. Staining images from spinal cord sections of the mice of control (top), at the peak stage (middle), and at the late stage (bottom), are shown. DPI and CS of each mouse are provided on the left. (B) Kv1.2 JXP clustering was altered in rrEAE lesions. Shown are staining images from spinal cord sections of the mice of control (top), at the peak stage (middle), and at the remitting stage (bottom). (C) Confocal image of the costaining of neurofilament (green) and Kv1.2 (red) along normal myelinated axon. White arrowheads, Kv1.2 JXP clusters. (D) Kvβ2 JXP clustering was disrupted in lesions of chEAE spinal cord. (E) Kvβ2 JXP clustering was disrupted in lesions of rrEAE spinal cord. Lesion areas are enclosed with dashed green lines and indicated with white arrows in merged images. (F) The expression of Kv1.2 in the areas with or without a lesion in spinal cord white matter at different stages of chEAE (left) and rrEAE (right). In chEAE, the average Kv1.2 staining intensities of spinal cord white matter are 667 ± 94 (AU, n = 18) in control areas, 703 ± 57 (AU, n = 13) in lesion areas from peak chEAE, and 571 ± 76 (AU, n = 15) in lesion areas from late chEAE. In rrEAE, the average Kv1.2 staining intensities are 653 ± 67 (AU, n = 16) in control areas, 571 ± 33 (AU, n = 15) in lesion areas from the peak stage, and 596 ± 43 (AU, n = 20) in lesion areas from the remitting stage. No significant difference was detected among the groups (One-Way ANOVA followed by Dunn's test, p > 0.05). Average fluorescence intensities of different areas of interest were measured, quantified, and shown as mean ± SEM. Background fluorescence intensity was subtracted. The result was obtained from at least three groups of mice. Scale bars, 200 μm in (A), (B), (D) and (E); 5 μm in (C).