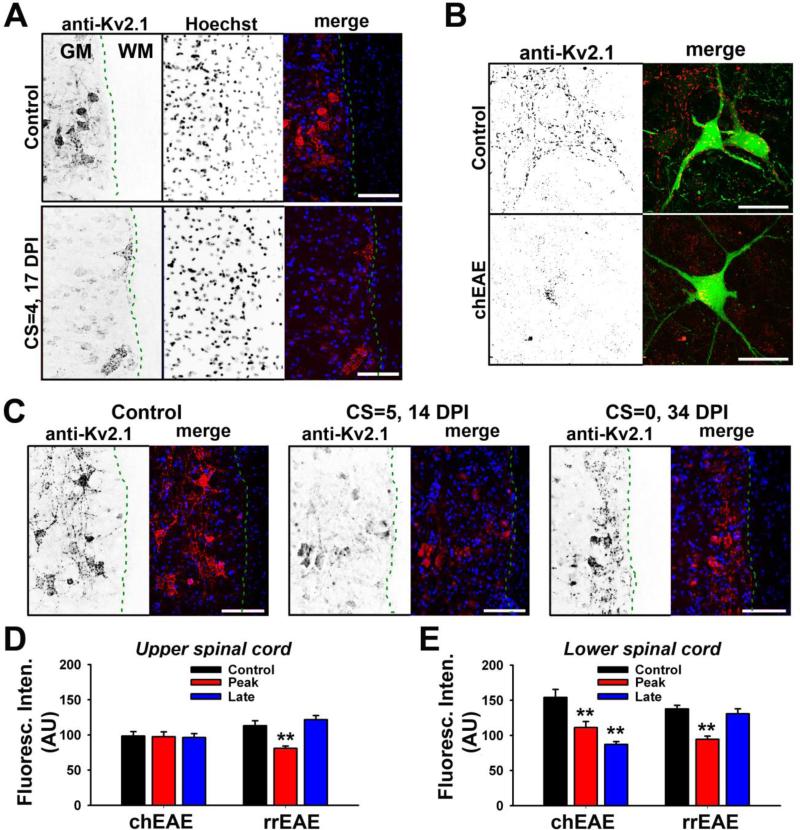
Figure 6. Alterations of somatodendritic Kv2.1 channels in spinal cord motor neurons in chEAE and rrEAE.
(A) Kv2.1 levels in motor neurons in lower spinal cord of chEAE were significantly reduced. Signals are inverted in single channel images. In merged images, Kv2.1 staining is shown in red and nuclear dye (Hoechst) staining in blue. DPI and CS are provided on the left. Dashed green lines indicate the border between gray matter (GM) and white matter (WM). (B) Reduction of somatodendritic Kv2.1 channels in motor neurons in EAE of Thy1:YFP transgenic mice. In merged images, YFP is shown in green and Kv2.1 staining in red. (C) Kv2.1 levels in motor neurons of lower spinal cord in rrEAE correlated with clinical signs. The rrEAE mice of control (left), at the peak phase (middle), and at the remitting phase (right), are shown. (D) Average Kv2.1 levels in motor neurons of upper spinal cord in chEAE (Control: 98 ± 6.4 (AU), n = 51; Peak: 97 ± 6.8 (AU), n = 55; Late: 96 ± 5.6 (AU), n = 54) and rrEAE (Control: 113 ± 6.9 (AU), n = 61; Peak: 81 ± 3.3 (AU), n = 63; Late (remitting): 122 ± 5.9 (AU), n = 63). (E) Average Kv2.1 levels in the motor neurons of lower spinal cord in chEAE and rrEAE. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test. ** p < 0.01. Scale bars, 150 μm in (A) and (C); 50 μm in (B).