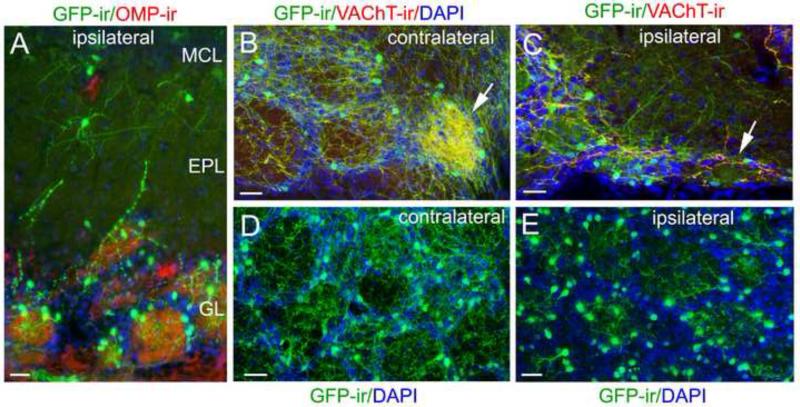
Figure 4. Ipsilateral olfactory peduncle lesion diminishes centrifugal cholinergic projections, allowing a better view of the intrinsic cholinergic system.
A: A representative confocal image of local cholinergic cells and nerve processes in the MCL, EPL and GL after surgery. The OB section was immunolabeled with the anti-OMP (red) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies and counterstained with DAPI (blue). GFP-ir centrifugal fibers in these layers are diminished, but there are many GFP-ir interneurons in the GL and some in the EPL and MCL. B: A confocal image of GFP-ir and VAChT-ir from a caudal-ventral OB region contralateral to the lesion, showing both several typical glomeruli and an atypical glomerulus, which receives dense cholinergic innervation (pointed by an arrow). C: Ipsilateral bulb section showing similar area of B. The dense cholinergic innervation in the atypical glomerulus was lost (pointed by an arrow). D: An representative image taken from a medial sagittal OB section contralateral to the lesion site, showing a patch of glomeruli. Individual glomeruli are outlined by DAPI staining (blue). There are numerous GFP-ir fibers within glomeruli and in surrounding regions. E: A representative image taken from an OB section ispilateral to the lesion site. DAPI nuclear staining (blue) outlines individual glomeruli. Note that GFP-ir fibers surrounding individual glomeruli are diminished. However, within the glomeruli there are many nerve processes that clearly emanate from local GFP-ir interneurons in the GL. Scale: 25 μm.