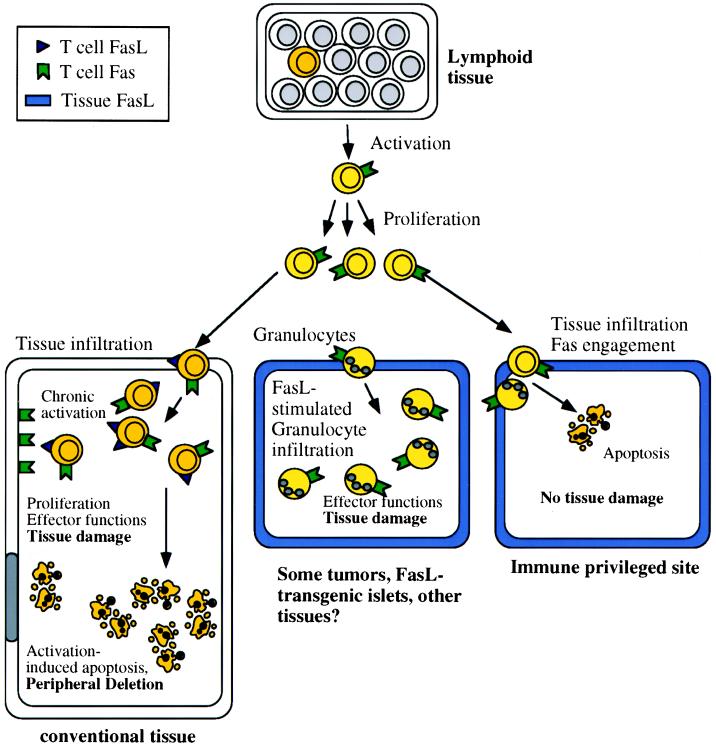
Figure 1.
Some immunological effects of FasL. Chronically activated T lymphocytes express both Fas and FasL, and in conventional tissues (Left) this can result in apoptotic death of the T cells (peripheral deletion) and induction of apoptosis in other Fas-expressing cells. Immunologically privileged tissues (Right) constitutively express FasL, and infiltrating T cells and granulocytes rapidly undergo apoptosis. Thus, the tissue is protected from any damage that might result from an immune response. In some tissues, however (Center), FasL induces a granulocytic infiltration, which can damage the tissue. The conditions that favor one or the other of these contrasting effects of tissue FasL are unknown.