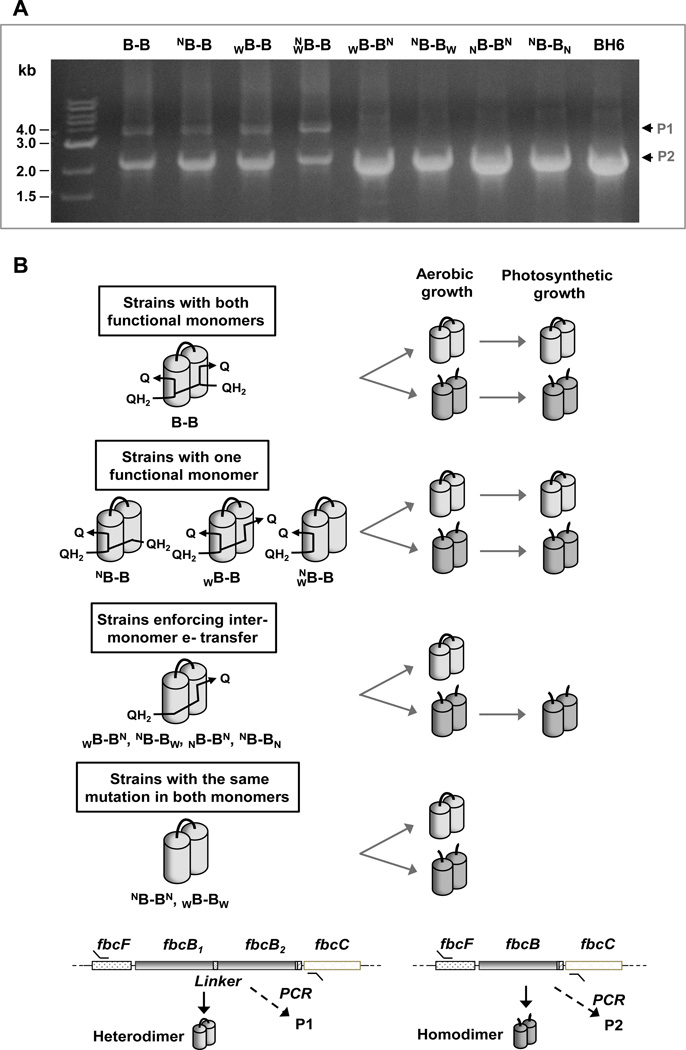
Fig. 4. Selection of functional bc1 complex variants for survival during growth.
(A) Constructs of fbc operon maintained at high abundance during photosynthetic growth. The bands represent PCR products amplified from photosynthetic cultures used in kinetic analysis. Both the heterodimeric construct (P1) and the recombinant homodimeric re-construct (P2) were maintained at high abundance in all strains with at least one functional monomer. On the other hand, in the strains which contained a mutation crippling monomeric function to enforce inter-monomer electron transfer, only the recombinant construct for the wild-type homodimer (P2) was maintained in the culture. The PCR bands from BH6 strain which contains a 6xHis-tagged homodimeric construct, was used as a control size marker. (B) Schematic representation of the selection of constructs coding for functional bc1 complex. The cultures of R. sphaeroides retain only the constructs expressing functional bc1 complex when bc1 complex is required for survival under anaerobic photosynthetic condition.